Coinhibitory Effects of Resveratrol- and Protopanaxadiol-Enriched Rice Seed Extracts Against Melanogenic Activities in Melan-a Cells
- PMID: 39683178
- PMCID: PMC11644661
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13233385
Coinhibitory Effects of Resveratrol- and Protopanaxadiol-Enriched Rice Seed Extracts Against Melanogenic Activities in Melan-a Cells
Abstract
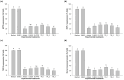
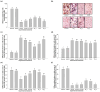
In the current study, we aimed to evaluate the combined antimelanogenic effects of resveratrol- and protopanaxadiol (PPD)-enriched rice seed extracts (DJ526 and DJ-PPD) in melan-a cells. The treatment antioxidant capacity was evaluated using the ABTS radical scavenging method. TR_3 (70% [wight (w)/w] of DJ526 and 30% [w/w] of DJ-PPD) markedly increased the antioxidant activity at a level similar to that of DJ526 and DJ-PPD alone. The antimelanogenic activities in melan-a cells were evaluated after co-culturing of treatments at the concentration of 100 μg/mL. The in vitro melan-a cell experiment showed that treatment with the DJ526 and DJ-PPD mixture significantly reduced the cellular tyrosinase activity and melanin content; suppressed the expression of melanogenesis-related genes and proteins; decreased the number and size of melanin-containing cells; upregulated phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and protein kinase B expression levels; and suppressed the expression of p-p38 MAPK. These results show that DJ-PPD does not interfere with the antioxidant and antimelanogeneic activities of DJ526 but enhances the antioxidant and antimelanogeneic activities of DJ526. These findings indicate the potential of resveratrol- and PPD-enriched rice seeds as novel agents for controlling hyperpigmentation.
Keywords: MAPK; NF-κB; antimelanogenic; antioxidant; hyperpigmentation; synergistic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



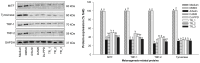

References
-
- Chung Y.C., Lee J.N., Kim B.S., Hyun C.-G. Anti-melanogenic effects of Paederia foetida L. extract via MAPK signaling-mediated MITF downregulation. Cosmetics. 2021;8:22. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics8010022. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

