Green Manure Rotation Combined with Biochar Application Improves Yield and Economic Stability of Continuous Cropping of Peppers in Southwest China
- PMID: 39683181
- PMCID: PMC11644829
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13233387
Green Manure Rotation Combined with Biochar Application Improves Yield and Economic Stability of Continuous Cropping of Peppers in Southwest China
Abstract
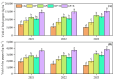
Crop rotation is widely recognized as a key strategy to mitigate the adverse effects associated with continuous cropping. Recent studies have demonstrated that biochar has a significant potential for preventing and controlling these challenges. However, the ameliorative effects of green manure rotation and biochar application on continuous pepper cultivation in the karst mountainous regions of Southwest China remain largely unexplored. To address this gap, a field experiment was conducted from 2020 to 2023 to investigate the effects of green manure rotation and biochar application on the continuous cropping of peppers. The experiment consisted of five treatments: CK (no green manure and no biochar), WP (winter fallow and conventional pepper production with chemical fertilization), GP (green manure and pepper rotation, the amount of fresh green manure returned to the field was about 15 t·ha-1), WP + B (winter fallow and pepper rotation with 1500 kg·ha-1 of biochar applied during the pepper season), and GP + B (green manure and pepper rotation with 1500 kg·ha-1 of biochar applied during the pepper season, the amount of fresh green manure returned to the field was about 15 t·ha-1). The results showed that all the improved measures (GP, WP + B, GP + B) increased the yield of fresh pepper and dry pepper by 26.97-72.98% and 20.96-65.70%, respectively, and the yield of dry pod pepper increased by 14.69-40.63% and 21.44-73.29% in 2021 to 2023, respectively, and significantly improved the yield stability and sustainability of continuous cropping of peppers compared with WP treatments. In addition, green manure rotation or biochar application alone or in combination enhanced the nutritional quality of pepper fruits by increasing the content of free amino acids (8.62-19.42%), reducing sugars (15.30-34.62%) and vitamin C (26.19-43.52), and decreasing the nitrate content (26.93-40.17%). Furthermore, the application of green manure rotation or biochar alone or in combination significantly improved the absorption of nitrogen (23.73-60.23%), phosphorus (18.12-61.71%), and potassium (20.57-61.48%) nutrients in the continuous cropping of peppers, which contributed to the improvement of fertilizer use efficiency. Notably, GP + B treatment not only improved the yield and quality of continuous cropping peppers but also resulted in higher production value and net income compared to the GP and WP + B treatments. In conclusion, the combination of green manure rotation and biochar application represents an effective strategy for mitigating the challenges of continuous cropping in pepper cultivation within the karst mountainous regions of Southwest China.
Keywords: green manure plowing and returning to the field; nutritional quality; obstacle soil; production sustainability; wine lees biochar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Liu Y., Xie M., Xue T., Sui X., Sun H., Li C., Song F. Short-term continuous cropping leads to a decline in rhizosphere soil fertility by modulating the perilla root exudates. Rhizosphere. 2024;32:100966. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2024.100966. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

