Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Pseudocereals with C3 and C4 Photosynthetic Metabolism in an Environment with Elevated CO2
- PMID: 39683246
- PMCID: PMC11644615
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13233453
Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Pseudocereals with C3 and C4 Photosynthetic Metabolism in an Environment with Elevated CO2
Abstract
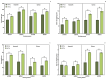
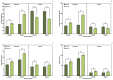
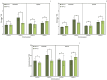
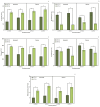
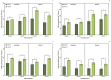
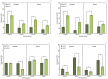
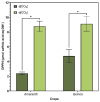
The present work aimed to investigate the effect of increasing CO2 concentration on the growth, productivity, grain quality, and biochemical changes in quinoa and amaranth plants. An experiment was conducted in open chambers (OTCs) to evaluate the responses of these species to different levels of CO2 {a[CO2] = 400 ± 50 μmol mol-1 CO2 for ambient CO2 concentration, e[CO2] = 700 ± 50 μmol mol-1 CO2 for the elevated CO2 concentration}. Growth parameters and photosynthetic pigments reflected changes in gas exchange, saccharolytic enzymes, and carbohydrate metabolism when plants were grown under e[CO2]. Furthermore, both species maintained most of the parameters related to gas exchange, demonstrating that the antioxidant system was efficient in supporting the primary metabolism of plants under e[CO2] conditions. Both species were taller and had longer roots and a greater dry weight of roots and shoots when under e[CO2]. On the other hand, the panicle was shorter under the same situation, indicating that the plants invested energy, nutrients, and all mechanisms in their growth to mitigate stress in expense of yield. This led to a reduction on panicle size and, ultimately, reducing quinoa grain yield. Although e[CO2] altered the plant's metabolic parameters for amaranth, the plants managed to maintain their development without affecting grain yield. Protein levels in grains were reduced in both species under e[CO2] in the average of two harvests. Therefore, for amaranth, the increase in CO2 mainly contributes to lowering the protein content of the grains. As for quinoa, its yield performance is also affected, in addition to its protein content. These findings provide new insights into how plants C3 (amaranth) and C4 (quinoa) respond to e[CO2], significantly increasing photosynthesis and its growth but ultimately reducing yield for quinoa and protein content in both species. This result ultimately underscore the critical need to breed plants that can adapt to e[CO2] as means to mitigate its negative effects and to ensure sustainable and nutritious crop production in future environmental conditions.
Keywords: Amaranthus spp.; Chenopodium quinoa (Willd); carbohydrate metabolism; climate change; photosynthetic parameters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hannah L. Climate Change Biology. 3rd ed. Academic Press; London, UK: 2021.
-
- IPCC . Climate Change: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. IPCC; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022.
-
- Letcher T.M. Global warming-a complex situation. Clim. Change Obs. Impacts Planet Earth Third Ed. 2021:3–17. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-821575-3.00001-3. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

