The Effectiveness and Safety of a Nutraceutical Combination in Overweight Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
- PMID: 39683371
- PMCID: PMC11643896
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16233977
The Effectiveness and Safety of a Nutraceutical Combination in Overweight Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
Background: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of a nutraceutical combination given to insulin-resistant overweight patients with altered lipid profiles. To this end, an observational study was designed in which 74 individuals (50 females and 24 males) underwent an observational period of 3 months.
Methods: During this time, a specific nutraceutical combination containing myo-inositol, glycine, Coprinus comatus, α-lipoic acid, phlorizin, zinc, vitamin B6, and chromium picolinate was administered. Patients were asked not to modify their lifestyles so that no variable that might interfere with results was introduced.
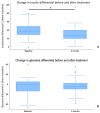
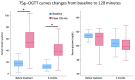
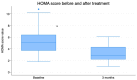
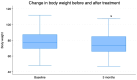
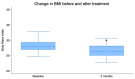
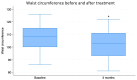
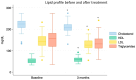
Results: After the 3-month period, the obtained data revealed that insulin levels significantly decreased with respect to the baseline, while glucose levels exhibited a trend towards lower concentrations, which was not significant. In addition, HOMA-IR index, body weight, BMI, and abdominal circumference values all decreased significantly. Regarding lipid profiles, the data obtained before and after the 3-month period showed statistically significant decreases in concentrations of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglyceride, as well as a small but statistically significant concomitant increase in HDL cholesterol.
Conclusions: Thus, on the basis of these data, it may be stated that the specific nutraceutical combination used in the present study significantly ameliorated a number of metabolic parameters without measurable side effects. The efficacy and safety of the product were, therefore, confirmed in our group of patients.
Keywords: insulin resistance; metabolic dysfunction; nutraceuticals; overweight.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Liu W., Yang X., Zhan T., Huang M., Tian X., Tian X., Huang X. Weight-adjusted waist index is positively and linearly associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Findings from NHANES 1999–2018. Front. Endocrinol. 2024;15:1457869. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1457869. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

