Diet Biofunctionality in Modulating Cardiovascular Parameters in Obese Patients After Bioenteric Intragastric Balloon Bariatric Surgery
- PMID: 39683432
- PMCID: PMC11643098
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16234038
Diet Biofunctionality in Modulating Cardiovascular Parameters in Obese Patients After Bioenteric Intragastric Balloon Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
Background/objectives: Adiposopathy is the cause of many secondary disorders in the function and structure of many organs and systems in the body. In the progression of obesity and the increasing dysfunction of anti-inflammatory me-diators, chronic inflammation occurs. This may be accompanied by the development of metabolic complications.
Methods: A diet with highly bioactive properties was formulated, and an element of diet therapy was introduced as a key component to support treatment in obese patients following bariatric surgery. Patients underwent a BIB (Bioenteric Intragastric Balloon) procedure. As obesity is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, this study aimed to regulate cardiovascular factors in adiposopathy. Anti-inflammatory dietary components with modulating properties were included, with increased bioflavonoids, vitamins A, E, C, folic acid, and synbiotics, and altered fatty acid composition.
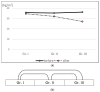
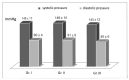
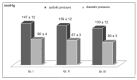
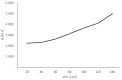
Results: The results showed satisfactory effects on fat reduction and the regulation of isoprostanes, plasminogen, angiotensin, prostacyclin, triglycerides, blood pressure, and blood rheology parameters. Cardiovascular co-morbidities are common in obesity. This is due to the endocrine function of adipocytes. As such, we decided to investigate the possibility of using bioactive dietary components as an adjunct to the safety of reducing prothrombotic parameters in obese patients after BIB surgery. This study hypothesised that the enrichment of the recommended diet after bariatric surgery with the addition of n-3 EFAs, bioflavonoids, vitamins, and synbiotics might result in comparable or greater fat mass loss in the subjects. In addition, the use of a functional diet might show a beneficial modifying effect on antihyperglycemic parameter values. We then compared the results to those obtained among patients fed a reducing, standard diet.
Conclusions: Using a functional diet, a significant reduction in visceral fat was achieved. A decrease in VFA was shown to reduce whole-blood viscosity. Furthermore, this study showed a significant effect of bioactive components on pro-thrombotic parameters in obese patients.
Keywords: angitensin; bariatric; blood rheology; dietotherapy; hypertension; isoprostanes; obesity; plasminogen activator inhitor-1; prostacyclins; triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this paper report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Czech A., Bernas M., Tatoń J. Cardiovascular symptoms of overweight and obesity. Endokrynol. Otyłość I Zaburzenia Przemiany Materii. 2007;3:85–94.
-
- Yue T., Sheng Q., Luo Y., Xiao Z., Wang Y., Song W., Yan M., Niu H., Zang T., Li N. Biflavonoids and Oligomeric Flavonoids from Food. In: Xiao J., Sarker S., Asakawa Y., editors. Handbook of Dietary Phytochemicals. Springer; Singapore: 2020. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

