Synthesis of 1,2,4-Oxadiazin-5(6 H)-One Derivatives and Their Biological Investigation as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
- PMID: 39683710
- PMCID: PMC11643077
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29235550
Synthesis of 1,2,4-Oxadiazin-5(6 H)-One Derivatives and Their Biological Investigation as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Abstract
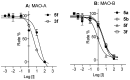
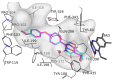
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) plays a key role in the pathogenesis of central nervous system disorders, and MAO inhibitors have been used in the treatment of depression and Parkinson's disease. In the search for new classes of MAO inhibitors, the present study investigated a series of 1,2,4-oxadiazin-5(6H)-one derivatives. This study provides the first optimization of the reaction conditions for the condensation of amidoximes with alkyl 2-halocarboxylates to yield the desired 1,2,4-oxadiazin-5(6H)-ones. The results of the in vitro MAO inhibition studies showed that the 1,2,4-oxadiazin-5(6H)-ones were indeed inhibitors of human MAO with the most potent inhibition observed for 5f (IC50 = 0.900 µM) and 7c (IC50 = 0.371 µM). It was concluded that, with appropriate substitution, 1,2,4-oxadiazin-5(6H)-one derivatives would act as good potency MAO-B inhibitors and lead compounds for the development of antiparkinsonian drugs. In Parkinson's disease, MAO-B inhibitors enhance central dopamine levels and reduce MAO-mediated production of hydrogen peroxide and resultant oxidative injury. This study represents one of few works to investigate synthetic approaches and biological activities of the 1,2,4-oxadiazin-5(6H)-one class of heterocycles.
Keywords: MAO; Parkinson’s disease; inhibition; monoamine oxidase; oxadiazine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

