Navigating the COVID-19 Therapeutic Landscape: Unveiling Novel Perspectives on FDA-Approved Medications, Vaccination Targets, and Emerging Novel Strategies
- PMID: 39683724
- PMCID: PMC11643501
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29235564
Navigating the COVID-19 Therapeutic Landscape: Unveiling Novel Perspectives on FDA-Approved Medications, Vaccination Targets, and Emerging Novel Strategies
Abstract
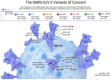
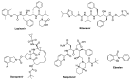
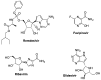
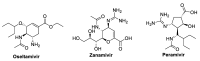
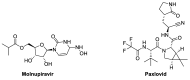
Amidst the ongoing global challenge of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the quest for effective antiviral medications remains paramount. This comprehensive review delves into the dynamic landscape of FDA-approved medications repurposed for COVID-19, categorized as antiviral and non-antiviral agents. Our focus extends beyond conventional narratives, encompassing vaccination targets, repurposing efficacy, clinical studies, innovative treatment modalities, and future outlooks. Unveiling the genomic intricacies of SARS-CoV-2 variants, including the WHO-designated Omicron variant, we explore diverse antiviral categories such as fusion inhibitors, protease inhibitors, transcription inhibitors, neuraminidase inhibitors, nucleoside reverse transcriptase, and non-antiviral interventions like importin α/β1-mediated nuclear import inhibitors, neutralizing antibodies, and convalescent plasma. Notably, Molnupiravir emerges as a pivotal player, now licensed in the UK. This review offers a fresh perspective on the historical evolution of COVID-19 therapeutics, from repurposing endeavors to the latest developments in oral anti-SARS-CoV-2 treatments, ushering in a new era of hope in the battle against the pandemic.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; drug repurposing; molnupiravir; paxlovid; vaccines; variant of concerns (VOC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Hong S.I., Ryu B.-H., Chong Y.P., Lee S., Kim S., Kim H.C., Hong K.-W., Bae I.-G., Cho O.-H. Five severe COVID-19 pneumonia patients treated with triple combination therapy with lopinavir/ritonavir, hydroxychloroquine, and interferon β-1b. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2020;56:106052. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

