Synthesis and Characterization of Na-P1 (GIS) Zeolite Using Rice Husk
- PMID: 39683755
- PMCID: PMC11643532
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29235596
Synthesis and Characterization of Na-P1 (GIS) Zeolite Using Rice Husk
Abstract
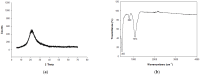
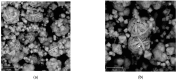
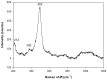
This work deals with the synthesis of Na-P1 (GIS) zeolite using rice husk as the starting material, instead of the more expensive chemicals currently used in the industry (i.e., Na aluminates and Na silicates). Rice husk is calcined at the temperature of 550 °C to obtain rice husk ash. Na-P1 is synthesized starting from rice husk ash, NaOH, and NaAlO2 by a protocol involving the mixing of a seed gel and a feedstock gel. Two synthesis runs are carried out at ambient pressure at the temperature of 110 °C by fixing the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio at 3.5 and 5.3, respectively. The synthesized products have been identified as well as the experiments developed by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. Then, the most successful synthesized powders were also characterized by infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, specific surface area (BET), and differential thermal analysis. The cell parameters are calculated using the Rietveld method. The combined Rietveld and reference intensity ratio methods allows us to exclude the presence of impurities and residual amorphous phase in the conducted experiments. Testing rice husk as a source of amorphous silica in the synthesis of Na-P1 represents both economic and environmental advantages. The high yields and the results of the experiment open the way for the transfer to an industrial production scale.
Keywords: rice husk; synthesis; zeolite Na-P1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Nery J.G., Mascarenhas Y.P., Cheetham A.K. A study of the highly crystalline, low-silica, fully hydrated zeolite P ion exchanged with (Mn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Sr2+, Ba2+) cations. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2003;57:229–248. doi: 10.1016/S1387-1811(02)00594-2. - DOI
-
- Albert B.R., Cheetham A.K., Stuart J.A., Adams C.J. Investigations on P zeolites: Synthesis, characterization, and structure of highly crystalline low-silica NaP. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 1998;21:133–142. doi: 10.1016/S1387-1811(97)00059-0. - DOI
-
- Baerlocher C., Meier W.M. The crystal structure of synthetic zeolite Na-P1, an isotope of gismondine. Z. Krist. 1971;135:339–354. doi: 10.1524/zkri.1972.135.5-6.339. - DOI
-
- Hansen S., Hakansson U., Landa-Canovas A.R., Falth L. On the crystal chemistry of NaP zeolites. Zeolites. 1993;13:276–280. doi: 10.1016/0144-2449(93)90006-O. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

