Enhancing Permanence of Corrosion Inhibitors Within Acrylic Protective Coatings for Outdoor Bronze Using Green Nanocontainers
- PMID: 39683863
- PMCID: PMC11643366
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29235702
Enhancing Permanence of Corrosion Inhibitors Within Acrylic Protective Coatings for Outdoor Bronze Using Green Nanocontainers
Abstract
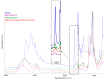
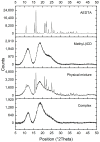
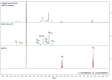
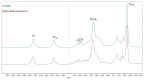
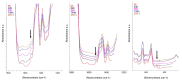
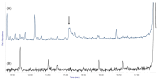
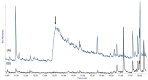
Outdoor bronze statues are constantly exposed to weather conditions and reactive compounds in the atmosphere that can interact with their surfaces. To avoid these interactions, a commonly used method is the application of coatings with corrosion inhibitors. However, a significant limitation of these inhibitors is their gradual loss over time. In this study, we aimed to improve the durability of 5-ethyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amine (AEDTA), the inhibitor chosen to formulate new acrylic coatings for outdoor bronzes. Methyl-β-cyclodextrin (Me-β-CD) was selected to host the inhibitor due to the capability of cyclodextrins to form complexes incorporating small organic molecules. The complexes of Me-β-CD and AEDTA were prepared and the inclusion of AEDTA was proved by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Then, acrylic coatings were prepared at different concentrations of the Me-β-CD/AEDTA system. They were thermally aged and monitored every 24 h. To evaluate the volatilization of the corrosion inhibitor, solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (SPME-GC/MS) and thermal desorption-GC/MS (TD-GC/MS) analyses were performed during the first 72 h. The results were compared to those of pure AEDTA films and Incralac®. The outcomes showed that Me-β-CD/AEDTA complexes are promising candidates for developing coatings with improved stability and longer retention of AEDTA.
Keywords: bronze statues; corrosion inhibitors; cyclodextrins; inclusion complexes; protective coatings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Salvadori B., Cagnini A., Galeotti M., Porcinai S., Goidanich S., Vicenzo A., Celi C., Frediani P., Rosi L., Frediani M. Traditional and Innovative Protective Coatings for Outdoor Bronze: Application and Performance Comparison. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018;135:46011. doi: 10.1002/app.46011. - DOI
-
- Letardi P. Testing New Coatings for Outdoor Bronze Monuments: A Methodological Overview. Coatings. 2021;11:131. doi: 10.3390/coatings11020131. - DOI
-
- Sherif E.M., Park S.-M. 2-Amino-5-ethyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole as a corrosion inhibitor for copper in 3.0% NaCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 2006;48:4065–4079. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2006.03.011. - DOI
-
- Casaletto M.P., Cirrincione C., Privitera A., Basilissi V. A Sustainable Approach to the Conservation of Bronze Artworks by Smart Nanostructured Coatings; Proceedings of the Interim Meeting of the ICOM.CC Metal Working Group; New Delhi, India. 26–30 September 2016.
-
- Pellis G., Giussani B., Letardi P., Poli T., Rizzi P., Salvadori B., Sansonetti A., Scalarone D. Improvement in the Sustainability and Stability of Acrylic Protective Coatings for Outdoor Bronze Artworks. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023;218:110575. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2023.110575. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

