Biotechnological 2-Phenylethanol Production: Recent Developments
- PMID: 39683919
- PMCID: PMC11644012
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29235761
Biotechnological 2-Phenylethanol Production: Recent Developments
Abstract
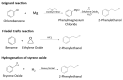
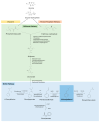
2-Phenylethanol (2-PE) is a key flavor compound with a rose-like scent, used in the cosmetics, perfume, home care and food industries. This aroma compound can be obtained naturally from various flowers, however chemical synthesis is the most used route to meet market demand. The increasing interest in natural products has led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives for 2-PE production through biotechnological approaches. The most efficient approach involves the biotransformation of L-phenylalanine into 2-PE via the Ehrlich pathway, a process observed in different microorganisms such as yeasts and bacteria. 2-PE produced by this way can be considered as natural. However, due to the toxicity of the aroma to the producing microorganism, low production yields are typically obtained, motivating efforts to develop production processes that can overcome this bottleneck, enhance 2-PE yields and reduce the production costs. This review presents and discusses the latest advances in the bioproduction of 2-PE through microbial fermentation, in terms of producing strains, the optimization of cultivation processes, strategies to mitigate product toxicity, and the use of low value feedstocks. Novel applications for 2-PE are also highlighted.
Keywords: 2-phenylethanol; bioproduction; in situ product removal techniques; low-cost feedstocks; microbial fermentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- 2-Phenylethanol Market to Hit $350 Million by 2027, Says Global Market Insights Inc. [(accessed on 6 March 2021)]. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2021/06/03/2241082/0/en/2-....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- LA/P/0008/2020 DOI 10.54499/LA/P/0008/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- UIDP/50006/2020 DOI 10.54499/UIDP/50006/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- UIDB/50006/2020 DOI 10.54499/UIDB/50006/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- UIDP/04378/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- UIDB/04378/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

