Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Volumetric Muscle Loss Regeneration
- PMID: 39684174
- PMCID: PMC11644721
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16233429
Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Volumetric Muscle Loss Regeneration
Abstract
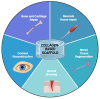
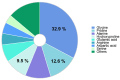
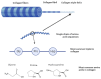
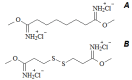
Volumetric muscle loss (VML) is a serious problem in healthcare that requires innovative solutions. Collagen and its derivatives are promising biomaterials for muscle tissue replacement due to their high biocompatibility, biodegradability, and lack of toxicity. This review comprehensively discusses collagen from various sources, its structural characteristics, cross-linking methods to obtain hydrogels, and approaches to incorporating various therapeutic molecules to create a biocomposite system with controlled release. Collagen-based scaffolds are promising constructs in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. They can both perform their function independently and act as a depot for various biologically active substances (drugs, growth factors, genetic material, etc.). Collagen-based scaffolds for muscle volume restoration are three-dimensional constructs that support cell adhesion and proliferation and provide controlled release of therapeutic molecules. Various mechanical and biological properties of scaffolds can be achieved by cross-linking agents and bioactive molecules incorporated into the structure. This review highlights recent studies on collagen-based hydrogels for restoration of volumetric muscle loss.
Keywords: collagen; hydrogel; regeneration; scaffold; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

