Advances and Challenges in Gene Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39684197
- PMCID: PMC11640776
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252312485
Advances and Challenges in Gene Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
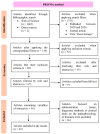
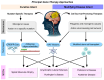
This review explores recent advancements in gene therapy as a potential treatment for neurodegenerative diseases, focusing on intervention mechanisms, administration routes, and associated limitations. Following the PRISMA procedure guidelines, we systematically analyzed studies published since 2020 using the PICO framework to derive reliable conclusions. The efficacy of various gene therapies was evaluated for Parkinson's disease (n = 12), spinal muscular atrophy (n = 8), Huntington's disease (n = 3), Alzheimer's disease (n = 3), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (n = 6). For each condition, we assessed the therapeutic approach, curative or disease-modifying potential, delivery methods, advantages, drawbacks, and side effects. Results indicate that gene therapies targeting specific genes are particularly effective in monogenic disorders, with promising clinical outcomes expected in the near future. In contrast, in polygenic diseases, therapies primarily aim to promote cell survival. A major challenge remains: the translation of animal model success to human clinical application. Additionally, while intracerebral delivery methods enhance therapeutic efficacy, they are highly invasive. Despite these hurdles, gene therapy represents a promising frontier in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, underscoring the need for continued research to refine and personalize treatments for each condition.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; curative genetic therapy; disease-modifying treatment; spinal muscular atrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wenceslau C.V., de Souza D.M., Mambelli-Lisboa N.C., Ynoue L.H., Araldi R.P., da Silva J.M., Pagani E., Haddad M.S., Kerkis I. Restoration of BDNF, DARPP32, and D2R Expression Following Intravenous Infusion of Human Immature Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Huntington’s Disease 3-NP Rat Model. Cells. 2022;11:1664. doi: 10.3390/cells11101664. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

