FLASH Radiotherapy: Benefits, Mechanisms, and Obstacles to Its Clinical Application
- PMID: 39684218
- PMCID: PMC11641130
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252312506
FLASH Radiotherapy: Benefits, Mechanisms, and Obstacles to Its Clinical Application
Abstract
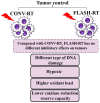
Radiotherapy (RT) has been shown to be a cornerstone of both palliative and curative tumor care. RT has generally been reported to be sharply limited by ionizing radiation (IR)-induced toxicity, thereby constraining the control effect of RT on tumor growth. FLASH-RT is the delivery of ultra-high dose rate (UHDR) several orders of magnitude higher than what is presently used in conventional RT (CONV-RT). The FLASH-RT clinical trials have been designed to examine the UHDR deliverability, the effectiveness of tumor control, the dose tolerance of normal tissue, and the reproducibility of treatment effects across several institutions. Although it is still in its infancy, FLASH-RT has been shown to have potential to rival current RT in terms of safety. Several studies have suggested that the adoption of FLASH-RT is very limited, and the incorporation of this new technique into routine clinical RT will require the use of accurate dosimetry methods and reproducible equipment that enable the reliable and robust measurements of doses and dose rates. The purpose of this review is to highlight the advantages of this technology, the potential mechanisms underpinning the FLASH-RT effect, and the major challenges that need to be tackled in the clinical transfer of FLASH-RT.
Keywords: FLASH radiotherapy; conventional radiotherapy; ionizing radiation; ultra-high dose rate.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Smyth L.M.L., Donoghue J.F., Ventura J.A., Livingstone J., Bailey T., Day L.R.J., Crosbie J.C., Rogers P.A.W. Comparative toxicity of synchrotron and conventional radiation therapy based on total and partial body irradiation in a murine model. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:12044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30543-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

