Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: A Potential Regulator of B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 39684227
- PMCID: PMC11641460
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252312515
Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: A Potential Regulator of B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
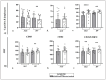
Autoimmune diseases represent a severe personal and healthcare problem that seeks novel therapeutic solutions. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent cells with interesting cell biology and promising therapeutic potential. The immunoregulatory effects of secretory factors produced by umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) were assessed on B lymphocytes from 17 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), as defined by the 2019 European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)/American College of Rheumatology (ACR) classification criteria for SLE, and 10 healthy volunteers (HVs). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients and HVs were cultured in a UC-MSC-conditioned medium (UC-MSCcm) and a control medium. Flow cytometry was used to detect the surface expression of CD80, CD86, BR3, CD40, PD-1, and HLA-DR on CD19+ B cells and assess the percentage of B cells in early and late apoptosis. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantified the production of BAFF, IDO, and PGE2 in PBMCs and UC-MSCs. Under UC-MSCcm influence, the percentage and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD19+BR3+ cells were reduced in both SLE patients and HVs. Regarding the effects of the MSC secretome on B cells in lupus patients, we observed a decrease in CD40 MFI and a reduced percentage of CD19+PD-1+ and CD19+HLA-DR+ cells. In contrast, in the B cells of healthy participants, we found an increased percentage of CD19+CD80+ cells and decreased CD80 MFI, along with a decrease in CD40 MFI and the percentage of CD19+PD-1+ cells. The UC-MSCcm had a minimal effect on B-cell apoptosis. The incubation of patients' PBMCs with the UC-MSCcm increased PGE2 levels compared to the control medium. This study provides new insights into the impact of the MSC secretome on the key molecules involved in B-cell activation and antigen presentation and survival, potentially guiding the development of future SLE treatments.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; B-cell activating factor receptor; mesenchymal stem cells; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Burki T.K. FDA approval for anifrolumab in patients with lupus. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021;3:e689. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00291-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

