Glioma-Derived Exosomes and Their Application as Drug Nanoparticles
- PMID: 39684236
- PMCID: PMC11641060
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252312524
Glioma-Derived Exosomes and Their Application as Drug Nanoparticles
Abstract
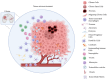
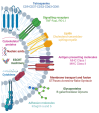
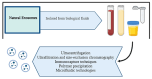
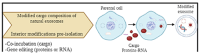
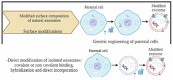
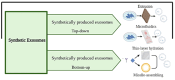
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive primary tumor of the Central Nervous System (CNS) with a low survival rate. The malignancy of GBM is sustained by a bidirectional crosstalk between tumor cells and the Tumor Microenvironment (TME). This mechanism of intercellular communication is mediated, at least in part, by the release of exosomes. Glioma-Derived Exosomes (GDEs) work, indeed, as potent signaling particles promoting the progression of brain tumors by inducing tumor proliferation, invasion, migration, angiogenesis and resistance to chemotherapy or radiation. Given their nanoscale size, exosomes can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB), thus becoming not only a promising biomarker to predict diagnosis and prognosis but also a therapeutic target to treat GBM. In this review, we describe the structural and functional characteristics of exosomes and their involvement in GBM development, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. In addition, we discuss how exosomes can be modified to be used as a therapeutic target/drug delivery system for clinical applications.
Keywords: exosomes; glioblastoma multiforme; glioma-derived exosomes; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Fulop J., Liu M., Blanda R., Kromer C., Wolinsky Y., Kruchko C., Barnhotlz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol. 2015;15:ii1–ii56. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

