Proteomic Markers of Aging and Longevity: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39684346
- PMCID: PMC11641128
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252312634
Proteomic Markers of Aging and Longevity: A Systematic Review
Abstract
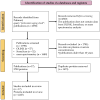
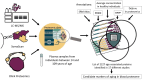
This article provides a systematic review of research conducted on the proteomic composition of blood as part of a complex biological age estimation. We performed a comprehensive analysis of 17 publicly available datasets and compiled an integral list of proteins. These proteins were sorted based on their detection probability using mass spectrometry in human plasma. We propose this list as a basis for creating a panel of peptides and quantifying the content of selected proteins in the format of a proteomic aging clock. The selected proteins are especially notable for their roles in inflammatory processes and lipid metabolism. Our findings suggest, for the first time, that proteins associated with systemic disorders, including those approved by the FDA for clinical use, could serve as potential markers of aging.
Keywords: aging; biological age; biomarkers; blood plasma proteome; high-copy proteins; knowledge databases; longevity; targeted mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

