Neurotrophic Effects of Foeniculum vulgare Ethanol Extracts on Hippocampal Neurons: Role of Anethole in Neurite Outgrowth and Synaptic Development
- PMID: 39684414
- PMCID: PMC11641539
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252312701
Neurotrophic Effects of Foeniculum vulgare Ethanol Extracts on Hippocampal Neurons: Role of Anethole in Neurite Outgrowth and Synaptic Development
Abstract
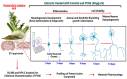
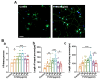
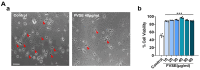
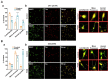
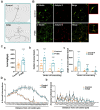
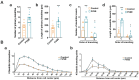
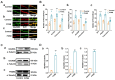
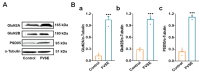
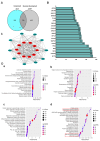
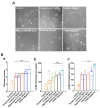
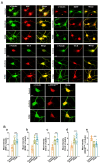
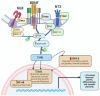
Foeniculum vulgare Mill, commonly known as fennel, is an aromatic herb traditionally used for culinary and medicinal purposes, with potential therapeutic effects on neurological disorders. However, limited research has focused on its neurotrophic impact, particularly on neuronal maturation and synaptic development. This study investigates the neurotrophic effects of F. vulgare ethanol extracts (FVSE) on the maturation of rat primary hippocampal neurons. Results show that FVSE and its prominent component, anethole, significantly promote neurite outgrowth in a dose-dependent manner. Optimal axonal and dendritic growth occurred at concentrations of 40 µg/mL FVSE and 20 µM anethole, respectively, without causing cytotoxicity, underscoring the safety of FVSE for neuronal health. Additionally, FVSE enhances the formation of synapses, essential for neuronal communication. Network pharmacology analysis revealed that FVSE components influence critical neurotrophic pathways, including PI3K-AKT and Alzheimer's disease pathways. Specifically, FVSE modulates key proteins, including tropomyosin receptor kinase (Trk), glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3βser9), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (Erk1/2). Anethole was found to play a key role in regulating these pathways, which was confirmed by immunocytochemistry experiments demonstrating its effect on promoting neuronal growth and synaptic development. In conclusion, this study highlights the neurotrophic properties of FVSE, with anethole emerging as a critical bioactive compound. These findings provide valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of fennel in treating neurological disorders, offering a basis for future research into interventions promoting neuronal growth and survival.
Keywords: Foeniculum vulgare Mill (FVSE); PI3K-AKT signaling pathway; anethole; hippocampal neurons; neurite outgrowth; neurodegenerative diseases; neurotrophic effects; neurotrophin signaling pathway; synaptic development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential Effects of the Processed and Unprocessed Garlic (Allium sativum L.) Ethanol Extracts on Neuritogenesis and Synaptogenesis in Rat Primary Hippocampal Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13386. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713386. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686193 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Anethole in Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Seed Ethanol Extract on Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in H9C2 Heart Myoblast Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;13(10):1161. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101161. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456415 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of fennel, and its major component trans-anethole against social isolation induced behavioral deficits in rats.Physiol Int. 2020 Mar;107(1):30-39. doi: 10.1556/2060.2020.00012. Physiol Int. 2020. PMID: 32491286
-
Exploring fennel (Foeniculum vulgare): Composition, functional properties, potential health benefits, and safety.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(20):6924-6941. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2176817. Epub 2023 Feb 19. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36803269 Review.
-
Genetics, genomics and breeding of fennel.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 May 7;25(1):595. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06608-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40335931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ivraghi M.S., Zamanian M.Y., Gupta R., Achmad H., Alsaab H.O., Hjazi A., Romero-Parra R.M., Alwaily E.R., Hussien B.M., Hakimizadeh E. Neuroprotective effects of gemfibrozil in neurological disorders: Focus on inflammation and molecular mechanisms. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024;30:e14473. doi: 10.1111/cns.14473. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morton H., Kshirsagar S., Orlov E., Bunquin L.E., Sawant N., Boleng L., George M., Basu T., Ramasubramanian B., Pradeepkiran J.A., et al. Defective mitophagy and synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on aging, mitochondria and synapse. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021;172:652–667. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.013. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

