The Involvement of Resolvins in Pathological Mechanisms of Periodontal Disease Associated with Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39684494
- PMCID: PMC11641189
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252312784
The Involvement of Resolvins in Pathological Mechanisms of Periodontal Disease Associated with Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review
Abstract
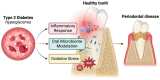
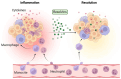
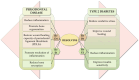
Resolvins are specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) derived from omega-3 fatty acids that play a critical role in resolving inflammation and restoring tissues to a state of health after an immune response. Their role in chronic inflammatory conditions highlights their importance in maintaining a balance between an effective immune response and the resolution of inflammation to prevent tissue damage. Periodontal disease is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth, leading to gum damage and bone loss. Chronic inflammation in periodontal disease can exacerbate systemic inflammation and influence other conditions, such as diabetes. There is a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease, as both are characterized by chronic inflammation and exacerbate systemic and oral health complications. This narrative review aims to synthesize the current knowledge on how resolvins influence inflammatory pathways and the tissue repair mechanism in periodontal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, this review serves as a foundation for developing targeted therapeutic strategies, addressing the pressing need for effective treatments that consider both systemic and oral health outcomes.
Keywords: inflammation; periodontal disease; resolvins; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pia M., Palo D., Rengo C., Fiorino A., Maurotto M., Gavinha Costa L., Manso M.C., Mosley G.A., Campos J., Fernandes H., et al. Correlation between Periodontitis and Gastritis Induced by Helicobacter pylori: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms. 2024;12:1579. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081579. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herrera D., Sanz M., Shapira L., Brotons C., Chapple I., Frese T., Graziani F., Hobbs F.D.R., Huck O., Hummers E., et al. Periodontal diseases and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and respiratory diseases: Summary of the consensus report by the European Federation of Periodontology and WONCA Europe. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2024;30:2320120. doi: 10.1080/13814788.2024.2320120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

