Monocyte/Macrophage-Specific Loss of ARNTL Suppresses Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Cardiac Impairment
- PMID: 39684718
- PMCID: PMC11641442
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252313009
Monocyte/Macrophage-Specific Loss of ARNTL Suppresses Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Cardiac Impairment
Abstract
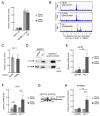
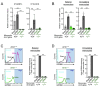
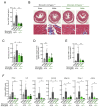
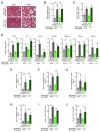
Defects in Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like 1 (ARNTL), a central component of the circadian clock mechanism, may promote or inhibit the induction of inflammation by monocytes/macrophages, with varying effects on different diseases. However, ARNTL's role in monocytes/macrophages under chronic kidney disease (CKD), which presents with systemic inflammation, is unclear. Here, we report that the expression of Arntl in monocytes promoted CKD-induced cardiac damage. The expression of G-protein-coupled receptor 68 (GPR68), which exacerbates CKD-induced cardiac disease, was regulated by ARNTL. Under CKD conditions, GPR68 expression was elevated via ARNTL, particularly in the presence of PU.1, a transcription factor specific to monocytes and macrophages. In CKD mouse models lacking monocyte-specific ARNTL, GPR68 expression in monocytes was reduced, leading to decreased cardiac damage and fibrosis despite no improvement in renal excretory capacity or renal fibrosis and increased angiotensin II production. The loss of ARNTL did not affect the expression of marker molecules, indicating the origin or differentiation of cardiac macrophages, but affected GPR68 expression only in cardiac macrophages derived from mature monocytes, highlighting the significance of the interplay between GPR68 and ARNTL in monocytes/macrophages and its influence on cardiac pathology. Understanding this complex relationship between circadian clock mechanisms and disease could help uncover novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: ARNTL; cardiac pathology GPR68; chronic kidney disease; circadian clock mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

