Squalene in Nanoparticles Improves Antiproliferative Effect on Human Colon Carcinoma Cells Through Apoptosis by Disturbances in Redox Balance
- PMID: 39684759
- PMCID: PMC11641743
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252313048
Squalene in Nanoparticles Improves Antiproliferative Effect on Human Colon Carcinoma Cells Through Apoptosis by Disturbances in Redox Balance
Abstract
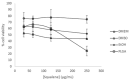
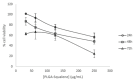
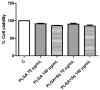
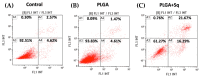
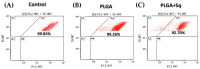
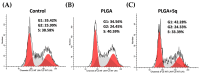
Squalene, a triterpene found in extra virgin olive oil, has therapeutic properties in diseases related to oxidative stress, such as cancer. However, its hydrophobic nature and susceptibility to oxidation limit its bioavailability outside of olive oil. To expand its applications, alternative delivery methods are necessary. The objective of the present study was to examine the impact of squalene encapsulated in PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid) nanoparticles (PLGA + Sq) on the proliferation of human colon carcinoma Caco-2 cells, as well as its underlying mechanism of action. The findings demonstrated that PLGA + Sq exert no influence on differentiated cells; however, it is capable of reducing the proliferation of undifferentiated Caco-2 cells through apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. This effect was initiated by the release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm and the subsequent activation of caspase-3. Furthermore, squalene exhibited pro-oxidant activity, as evidenced by an increase in intracellular ROS (reactive oxygen species) levels. The results of the squalene effect on genes associated with cell death, inflammation, and the cell cycle indicate that its antiproliferative effect may be post-transcriptional. In conclusion, PLGA + Sq demonstrate an antiproliferative effect on Caco-2 cells through apoptosis by altering redox balance, suggesting squalene's potential as a functional food ingredient for colorectal cancer prevention.
Keywords: Caco-2 cells; PLGA; ROS; apoptosis; nanoparticles; squalene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Taheri E., Ghorbani S., Safi M., Sani N.S., Amoodizaj F.F., Heidari M., Chavoshi R., Hajazimian S., Isazadeh A., Heidari M. Inhibition of Colorectal Cancer Cell Line CaCo-2 by Essential Oil of Eucalyptus Camaldulensis through Induction of Apoptosis. Acta Med. Iran. 2020;58:260–265. doi: 10.18502/acta.v58i6.4051. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PID2022-136414OB-I00/The Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación-Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional
- B16_23R/Fondo Social Europeo-Gobierno de Aragón
- PRTR-C17.I1/Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation with funds from the European Union NextGeneration EU, from the Recovery, Transformation and Resilience Plan
- CB06/03/1012/CIBER Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y la Nutrición as an initiative of FEDER-ISCIII:CIBEROBN
- NEWPOWER, S1/1.1/E01116;/Interreg Sudoe Program:
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

