Perspectives of Quantitative GC-MS, LC-MS, and ICP-MS in the Clinical Medicine Science-The Role of Analytical Chemistry
- PMID: 39685736
- PMCID: PMC11641993
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13237276
Perspectives of Quantitative GC-MS, LC-MS, and ICP-MS in the Clinical Medicine Science-The Role of Analytical Chemistry
Abstract
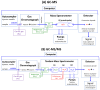
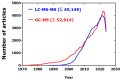
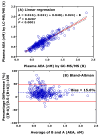
Mass spectrometry (MS) is the only instrumental analytical technology that utilizes unique properties of matter, that is, its mass (m) and electrical charge (z). In the magnetic and/or electric fields of mass spectrometers, electrically charged native or chemically modified (millions) endogenous and (thousands) exogenous substances, the analytes, are separated according to their characteristic mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) values. Mass spectrometers coupled to gas chromatographs (GC) or liquid chromatographs (LC), the so-called hyphenated techniques, i.e., GC-MS and LC-MS, respectively, enable reliable determination of the concentration of analytes in complex biological samples such as plasma, serum, and urine. A particular technology is represented by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), which is mainly used for the analysis of metal ions. The highest analytical accuracy is reached by using mass spectrometers with high mass resolution (HR) or by tandem mass spectrometers, as it can be realized with quadrupole-type instruments, such as GC-MS/MS and LC-MS/MS, in combination with stable-isotope labeled analytes that serve as internal standards, like a standard weight in scales. GC-MS belongs to the oldest and most advanced instrumental analytical technology. From the very beginning, GC-MS found broad application in basic and applied research sciences. GC-MS has played important roles in discovering biochemical pathways, exploring underlying mechanisms of disease, and establishing new evidence-based pharmacological therapy. In this article, we make an inventory of the use of instrumental mass spectrometry in the life sciences and attempt to provide a perspective study on the future of analytical mass spectrometry in clinical science, mainly focusing on GC-MS and LC-MS. We used information freely available in the scientific database PubMed (retrieved in August-November 2024). Specific search terms such as GC-MS (103,000 articles), LC-MS (113,000 articles), and ICP-MS (14,000 articles) were used in the Title/Abstract in the "PubMed Advanced Search Builder" including filters such as search period (1970-2024). In total, around 103,000 articles on GC-MS, 113,000 articles on LC-MS (113,000), and 14,000 articles on ICP-MS were found. In the period 1995-2023, the yearly publication rate accounted for 3042 for GC-MS articles and 3908 for LC-MS articles (LC-MS/GC-MS ratio, 1.3:1). Our study reveals that GC-MS/MS, LC-MS/MS, and their high-resolution variants are indispensable instrumentations in clinical science including clinical pharmacology, internal and forensic medicine, and doping control. Long-tradition manufacturers of analytical instruments continue to provide increasingly customer-friendly GC-MS and LC-MS apparatus, enabling fulfillment of current requirements and needs in the life sciences. Quantitative GC-MS and GC-MS/MS methods are expected to be used worldwide hand in hand with LC-MS/MS, with ICP-MS closing the gap left for metal ions. The significance of analytical chemistry in clinical science in academia and industry is essential.
Keywords: analytical chemistry; clinical medicine; gas chromatography; life sciences; liquid chromatography; mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interpretation of negative-ion chemical ionization GC-MS and GC-MS/MS mass spectra of perfluorinated organic analyte derivatives: Consideration of reduction reactions in the gas phase.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025 Mar 1;1253:124487. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2025.124487. Epub 2025 Jan 28. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39892334
-
Comparison of GC-NCI MS, GC-ICP-MS, and GC-EI MS-MS for the determination of PBDEs in water samples according to the Water Framework Directive.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Oct;407(26):8009-18. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-8973-y. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26319281
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
-
Role of liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HR/MS) in clinical toxicology.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2012 Sep;50(8):733-42. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2012.713108. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2012. PMID: 22888997 Review.
-
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination and profiling of prohibited steroids in human biological matrices. A review.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 May 15;927:22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23317577 Review.
Cited by
-
Croton bonplandianus leaves extract to mitigate the hazardous effect of Meloidogyne incognita: GC-MS and molecular docking analysis of nematicidal compounds.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 13;15(25):20200-20210. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00931f. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40519688 Free PMC article.
-
Functional metabolomics: unlocking the role of small molecular metabolites.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 9;12:1542100. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1542100. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40703706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wei D., Horton K., Chen J., Dong L., Chen S., Abdul-Hadi K., Zhang T., Casson C., Shaw M., Shiraishi T., et al. Development of a Highly Sensitive Hybrid LC/MS Assay for the Quantitative Measurement of CTLA-4 in Human T Cells. Molecules. 2023;28:3311. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083311. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Molteni L., Charlier B., Izzo V., Coglianese A., Conti V., Eleopra R., Cilia R., Capelli C., D’Urso A., de Grazia U. Development and Validation of a New LC-MS/MS Bioanalytical Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Levodopa, Levodopa Methyl Ester, and Carbidopa in Human Plasma Samples. Molecules. 2023;28:4264. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

