Blood-Based Clinical Biomarkers of Inflammation and Nutrition in Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- PMID: 39685747
- PMCID: PMC11642226
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13237289
Blood-Based Clinical Biomarkers of Inflammation and Nutrition in Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Abstract
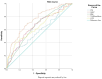
Background: In this study, the aim was to investigate blood-based clinical biomarkers of inflammation and nutrition indices in hyperemesis gravidarum (HG). Methods: This retrospective case-control study was conducted at a tertiary hospital between 2018 and 2022. A total of 820 pregnant women were enrolled in this study; 410 pregnant women were diagnosed with HG (HG group) at 6-14 weeks of gestation, and 410 pregnant women were healthy controls (control group) in the same gestational weeks. Patients' demographic and clinical characteristics and laboratory parameters were recorded. The hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score, the modified-HALP (m-HALP) score, and the prognostic nutritional index (PNI) were calculated. Results: The HALP score (32.6 (IQR: 24.9-41.5) vs. 39.2 (IQR: 30.8-49.2), p < 0.001) and the PNI score (50 (IQR: 46.3-53.6) vs. 51.3 (IQR: 48.6-53.8), p < 0.001) were significantly lower in the HG group, whereas the m-HALP score was similar between the groups. The HALP score had an AUC of 0.625 (95% CI: 0.586-0.664), with the optimal cut-off value set at 35.8, resulting in a sensitivity of 59.7% and a specificity of 59.5% (p < 0.001). Similarly, the PNI score showed an AUC of 0.580 (95% CI: 0.541-0.619), and the optimal cut-off value was set at 50.6, resulting in a sensitivity of 54.9% and a specificity of 54.9% (p < 0.001). In regression analysis, lower HALP scores (OR: 0.906, 95% CI: 0.833-0.984, p = 0.019) and lower PNI scores (OR: 0.941, 95% CI: 0.891-0.995, p = 0.033) were significantly associated with HG, highlighting their potential as diagnostic markers. Additionally, a negative statistically significant correlation was observed between PNI scores and ketonuria (r = -0.073, p = 0.036). Conclusions: This study demonstrated a decrease in the HALP score and PNI score in cases of HG. However, the m-HALP score was similar in the HG and control groups.
Keywords: HALP score; hyperemesis gravidarum; inflammation; m-HALP score; nutrition; prognostic nutritional index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources