A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor in Patients Using Left Ventricular Assist Devices
- PMID: 39685874
- PMCID: PMC11641912
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13237418
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor in Patients Using Left Ventricular Assist Devices
Abstract
Background: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2-i) have been shown to reduce risks of clinical events in patients with heart failure (HF). However, data on the use of SGLT2-i in patients with left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) are scarce. We thought to assess the efficacy and safety of SGLT2-i in patients with LVADs. Methods: A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane from inception to November 2024. We used all relevant words for "SGLT2-i" and "LVAD" to search in databases, and we included studies and published abstracts in peer-reviewed journals of studies that assessed SGLT2-i in patients with LVAD. Results: Four studies and seven abstracts totaling 228 patients using SGLT2-i were included. Empagliflozin, Dapagliflozin, and Canagliflozin were the used SGLT2-i across the included studies. Pooled analysis showed that SGLT2-i significantly improved ejection fraction (EF) (Mean= 4.2, 95% CI [1.22, 7.19]) and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) (Mean = -0.44, 95% CI [-0.79, -0.09]) from baseline. However, no significant changes in B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), or glomerular filtration rate (GFR) were noticed. Other outcomes of interest not included in the meta-analysis did not show significant changes, such as cardiac index (CI), left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVESD), left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), mean arterial pressure (MAP), or mean pulmonary artery pressure (MPAP). The pooled percentage of people with driveline infection was 9%, 95% CI (3, 19). Conclusions: SGLT2-i effectively improves EF and HbA1c in patients using LVAD. Further adequately powered randomized studies are warranted to ascertain its clinical efficacy and safety in that unique population.
Keywords: efficacy; meta-analysis; safety; sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors; systematic review; ventricular assist device.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


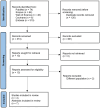
References
-
- McMurray J.J.V., Solomon S.D., Inzucchi S.E., Kober L., Kosiborod M.N., Martinez F.A., Ponikowski P., Sabatine M.S., Anand I.S., Belohlavek J., et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;381:1995–2008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911303. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tromp J., Ponikowski P., Salsali A., Angermann C.E., Biegus J., Blatchford J., Collins S.P., Ferreira J.P., Grauer C., Kosiborod M., et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibition in patients hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure: Rationale for and design of the EMPULSE trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021;23:826–834. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2137. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Packer M., Butler J., Zannad F., Filippatos G., Ferreira J.P., Pocock S.J., Carson P., Anand I., Doehner W., Haass M., et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Worsening Heart Failure Events in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction: EMPEROR-Preserved Trial. Circulation. 2021;144:1284–1294. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chavali S., Barua S., Adji A., Robson D., Raven L.M., Greenfield J.R., Eckford H., Macdonald P.S., Hayward C.S., Muthiah K. Safety and tolerability of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in bridge-to-transplant patients supported with centrifugal-flow left ventricular assist devices. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023;391:131259. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.131259. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

