Phased Array Antenna Calibration Based on Autocorrelation Algorithm
- PMID: 39686033
- PMCID: PMC11644803
- DOI: 10.3390/s24237496
Phased Array Antenna Calibration Based on Autocorrelation Algorithm
Abstract
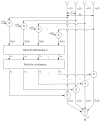
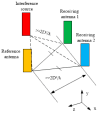
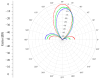
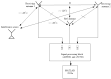
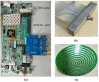
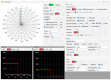
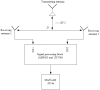
The problem of calibrating phased array antennas in a noisy environment using an autocorrelation algorithm is investigated and a mathematical model of the autocorrelation calibration method is presented. The proposed calibration system is based on far-field scanning of the phased array antenna in an environment with internal noise and external interference. The proposed method is applied to a phased array antenna and compared with traditional rotating-element electric-field vector methods, which involve identifying the maximum and minimum vector-sum points (REVmax and REVmin, respectively). The proposed calibration system is verified for a phased array antenna at 3 GHz. Experimental verification of the mathematical model of the proposed method demonstrates that the autocorrelation method is more accurate than the rotating-element electric-field vector methods in determining the amplitude and phase shifts. The measured peak gain of the combined beam in the E-plane increased from 7.83 to 8.37 dB and 3.57 to 4.36 dB compared to the REVmax and REVmin methods, respectively, and the phase error improved from 47° to 55.48° and 19.43° to 29.16°, respectively. The proposed method can be considered an effective solution for large-scale phase calibration at both in-field and in-factory levels, even in the presence of external interference.
Keywords: amplitude error; autocorrelation algorithm; far-field probe; phase error; phased array antenna; radiation pattern.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Li X., Zhang L., Cheng L., Zhu J., Wu J. Design of micro-phased array antenna control system; Proceedings of the 2021 2nd China International SAR Symposium (CISS); Shanghai, China. 2–4 November 2021; Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE; 2021. pp. 1–5. - DOI
-
- Yang G., Zhang Y., Zhang S. Wide-Band and Wide-Angle Scanning Phased Array Antenna for Mobile Communication System. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021;2:203–212. doi: 10.1109/OJAP.2021.3057062. - DOI
-
- Abdel-Wahab W.M., Palizban A., Ehsandar A., Safavi-Naeini S. SIW-Feed for 20 GHz Active Phased Array (1024-Element) Antenna with Modular Architecture; Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and North American Radio Science Meeting; Montreal, QC, Canada. 5–10 July 2020; Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE; 2020. pp. 629–630. - DOI
-
- Kozhakhmetova B. Development and Research of Phased Array Antenna Control Unit for Educational Purposes; Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 4th International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST); Astana, Kazakhstan. 15–17 May 2024; Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE; 2024. pp. 44–47. - DOI
-
- Temir K., Akyüz M.S., Alp Y.K. Consideration of environmental and functional factors in calibration of antenna integrated active phased array transmitters; Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology (PAST); Waltham, MA, USA. 18–21 October 2016; Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE; 2016. pp. 1–5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

