Room-Temperature Ammonia Sensing Using Polyaniline-Coated Laser-Induced Graphene
- PMID: 39686369
- PMCID: PMC11644887
- DOI: 10.3390/s24237832
Room-Temperature Ammonia Sensing Using Polyaniline-Coated Laser-Induced Graphene
Abstract
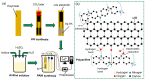
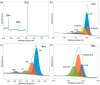
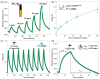
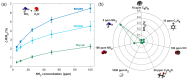
The reliable detection of ammonia at room temperature is crucial for not only maintaining environmental safety but also for reducing the risks of hazardous pollutants. In this study, the electrochemical modification of laser-induced graphene (LIG) with polyaniline (PANI) led to the development of a chemo-resistive nanocomposite (PANI@LIG) for detecting ammonia levels at room temperature. The composite is characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transforms infrared, and Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. This work marks the first utilization of PANI@LIG for gas sensing and introduces a simple but effective approach for fabricating low-cost wearable gas sensors with high sensitivity and flexibility.
Keywords: ammonia; gas sensing; laser-induced graphene; polyaniline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Mbayachi V.B., Ndayiragije E., Sammani T., Taj S., Mbuta E.R., Khan A.U. Graphene Synthesis, Characterization and Its Applications: A Review. Results Chem. 2021;3:100163. doi: 10.1016/j.rechem.2021.100163. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2023 FI-2 00180/AGAUR-Personal Investigador Predoctoral en Formació (FI) ajuts Predoctoral Program
- 823895-PE/H2020-MSCA-RISE-2018: Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions
- PDC2022- 133967-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (MICINN)
- TED2021-131442B-C31/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (MICINN)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

