Harnessing microbial heterogeneity for improved biosynthesis fueled by synthetic biology
- PMID: 39686977
- PMCID: PMC11646789
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.11.004
Harnessing microbial heterogeneity for improved biosynthesis fueled by synthetic biology
Abstract
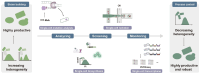
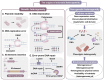
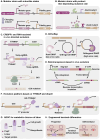
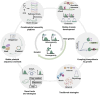
Metabolic engineering-driven microbial cell factories have made great progress in the efficient bioproduction of biochemical and recombinant proteins. However, the low efficiency and robustness of microbial cell factories limit their industrial applications. Harnessing microbial heterogeneity contributes to solving this. In this review, the origins of microbial heterogeneity and its effects on biosynthesis are first summarized. Synthetic biology-driven tools and strategies that can be used to improve biosynthesis by increasing and reducing microbial heterogeneity are then systematically summarized. Next, novel single-cell technologies available for unraveling microbial heterogeneity and facilitating heterogeneity regulation are discussed. Furthermore, a combined workflow of increasing genetic heterogeneity in the strain-building step to help in screening highly productive strains - reducing heterogeneity in the production process to obtain highly robust strains (IHP-RHR) facilitated by single-cell technologies was proposed to obtain highly productive and robust strains by harnessing microbial heterogeneity. Finally, the prospects and future challenges are discussed.
Keywords: Genetic heterogeneity; Highly productive strains; Highly robust strains; Non-genetic heterogeneity; Single-cell technologies; Synthetic biology.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

