Research Trends and Hotspots on Asthma and Depression: A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 39687059
- PMCID: PMC11648539
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S495814
Research Trends and Hotspots on Asthma and Depression: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Asthma and depression are prevalent conditions with significant comorbidity, impacting patients' quality of life. This bibliometric study aims to analyze research trends and hotspots in the field from 2000 to 2023, identifying key contributions and predicting future directions.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search in the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) for articles on asthma and depression, published between 2000 and 2023. Bibliometrics, which involves the application of mathematical and statistical methods to analyze scholarly literature, was employed in this study to systematically assess the research trends and hotspots in the field of asthma and depression. VOSviewer and CiteSpace software were utilized for visual analysis and data visualization, enabling us to map collaboration networks and identify research hotspots and trends within the asthma and depression literature.
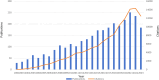
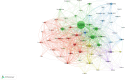
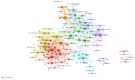
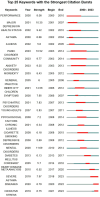
Results: Our analysis retrieved 3067 papers from 937 journals, involving 14,631 authors and 4006 institutions across 106 countries. The United States, Columbia University, the Journal of Asthma, and Christer Janson were the most prolific contributors. Six primary research themes emerged: quality of life, childhood asthma, primary care, substance P, intervention, and emotion. Additionally, Burst detection analysis identified emerging topics, including severe asthma, other respiratory diseases, and oxidative stress.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis has revealed significant insights into the research trends and hotspots in the field of asthma and depression. The primary findings indicate a growing body of research highlighting the impact of depression on asthma control and patients' quality of life, the need for psychological interventions in treating comorbid asthma and depression, and the emerging focus on severe asthma and oxidative stress mechanisms. These findings underscore the importance of continued research in these areas to advance our understanding and improve clinical outcomes for patients with these comorbid conditions.
Keywords: asthma; bibliometric analysis; depression; hotspots; research trends.
© 2024 Peng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

