Enhanced anticancer and biological activities of environmentally friendly Ni/Cu-ZnO solid solution nanoparticles
- PMID: 39687105
- PMCID: PMC11647829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39912
Enhanced anticancer and biological activities of environmentally friendly Ni/Cu-ZnO solid solution nanoparticles
Abstract
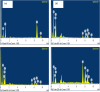
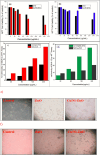
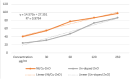
The study investigates the impact of incorporating Ni and Cu into the lattice of ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) to enhance their anticancer and antioxidant properties. Characterization techniques including pXRD, FTIR, UV-visible absorption spectroscopy, FESEM, and EDAX confirm the successful synthesis and structural modifications of Ni/Cu-ZnO NPs. Anticancer activity against breast cancer (MDA) and normal skin (BHK-21) cells reveals dose-dependent cytotoxicity, with Ni/Cu-ZnO NPs exhibiting higher efficacy against MDA cells while being less harmful to BHK-21 cells. Morphological studies corroborate these findings. Additionally, antioxidant assays using TAC, FRAP, and DPPH assay demonstrate the superior antioxidant activity of Ni/Cu-ZnO NPs matched to pure ZnO. Overall, the synergistic effect of Ni and Cu incorporation leads to improved therapeutic potential, making Ni/Cu-ZnO NPs promising candidates for cancer therapy and antioxidant applications. Molecular docking recreations were performed using Auto Dock Vina software to gain more insights and validate the observed biological activities of un-doped ZnO and bi-metal doped ZnO NPs, we investigated the interaction and binding affinities of pure ZnO and bimetallic metal co-doped ZnO for their antioxidant and anticancer studies. Ni/Cu-ZnO have shown good antioxidants and exhibited remarkable anticancer activities.
Keywords: Anticancer; Antioxidant activities; Band gap tuning; Solid solutions; ZnO NPs.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



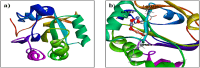
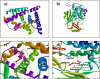
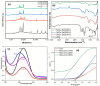


References
-
- Wiesmann N., Tremel W., Brieger J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for therapeutic purposes in cancer medicine. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2020;8(23):4973–4989. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z., Ma Y., Zhao H., Yuan Y., Kim B.Y. Nanotechnology platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020;12(2):e1590. - PubMed
-
- Wicki A., Witzigmann D., Balasubramanian V., Huwyler J. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J. Contr. Release. 2015;200:138–157. - PubMed
-
- Ostrovsky S., Kazimirsky G., Gedanken A., Brodie C. Selective cytotoxic effect of ZnO nanoparticles on glioma cells. Nano Res. 2009;2:882–890.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

