The association between moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and health-related quality of life in Chinese adolescents: the mediating roles of emotional intelligence and perceived stress
- PMID: 39687563
- PMCID: PMC11646723
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1477018
The association between moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and health-related quality of life in Chinese adolescents: the mediating roles of emotional intelligence and perceived stress
Abstract
Introduction: Chinese adolescents are facing tremendous academic pressure and challenges brought about by changes in the social environment, which pose a serious threat to their health-related quality of life (HRQOL). This cross-sectional survey uses convenience and snowball sampling to explore the relationship between adolescents' HRQOL and their participation in moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA).
Methods: This study subjects include 440 adolescents aged 12 to 18, from four youth training centers and three schools in the central regions of Hunan, Hubei, and Henan provinces, chosen as representative samples for this study. We used AMOS v.26 to construct a structural equation model for data analysis and hypothesis testing.
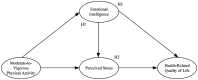
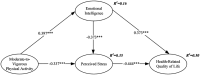
Results: The results indicated that active participation in MVPA helps reduce adolescents' perceived stress and enhances their emotional intelligence and HRQOL levels. Specifically, MVPA weakens adolescents' perceived stress through the mediating role of emotional intelligence (coefficient = -0.148, p < 0.001), and perceived stress also mediates the relationship between emotional intelligence and HRQOL (coefficient = 0.165, p < 0.001). Furthermore, the positive impact of MVPA on HRQOL is mediated by emotional intelligence and perceived stress (coefficient = 0.363, p < 0.001). The explanatory power of this study is R 2 = 0.50.
Conclusion: The study results indicate that MVPA has a positive impact on the HRQOL levels of Chinese adolescents. Physical activity, especially moderate-to-vigorous intensity exercise, should be considered a strategic approach to maintaining HRQOL among adolescents. Society, schools, and families should create an environment conducive to physical exercise to support adolescents in engaging in physical activities and developing a healthy lifestyle.
Keywords: adolescents; emotional intelligence; health-related quality of life; moderate-to-vigorous physical activity; perceived stress.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Li, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bermejo-Cantarero A., Álvarez-Bueno C., Martínez-Vizcaino V., Redondo-Tébar A., Pozuelo-Carrascosa D. P., Sánchez-López M. (2021). Relationship between both cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness and health-related quality of life in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Health. Qual. Life Out. 19:127. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01766-0, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources