Avenanthramide-C ameliorate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via modulating Akt/GSK-3β and Wnt-4/β-Catenin pathways in male rats
- PMID: 39687571
- PMCID: PMC11646862
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1507786
Avenanthramide-C ameliorate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via modulating Akt/GSK-3β and Wnt-4/β-Catenin pathways in male rats
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Avenanthramide-C ameliorate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via modulating Akt/GSK-3β and Wnt-4/β-Catenin pathways in male rats.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 9;12:1601841. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1601841. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40417061 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Doxorubicin (DOX) drugs used in cancer treatment can cause various adverse effects, including hepatotoxicity. Natural-derived constituents have shown promising effects in alleviating chemotherapy-induced toxicities. This study addressed the effect of Avenanthramides-C (AVN-C) treatment in rats with DOX-indued hepatotoxicity.
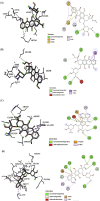
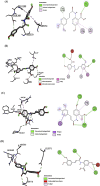
Methods: AutoDock Vina was used for the molecular docking investigations. In silico toxicity prediction for AVN-C and DOX was performed using the Pro Tox-III server. Four groups of ten male Sprague-Dawley rats were created: Group 1 (Gp1) served as a negative control, Gp2 received an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of AVN-C (10 mg/kg), Gp3 received an i.p. dose of DOX (4 mg/kg) weekly for a month, and Gp4 received the same dose of DOX as G3 and AVN-C as G2. Histopathological, molecular, and biochemical analyses were conducted 1 month later.
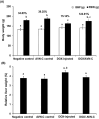
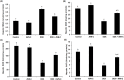
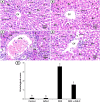
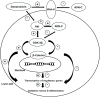
Results: The study showed that treatment with AVN-C significantly ameliorated DOX-induced hepatotoxicity in rats by restoring biochemical alterations, boosting antioxidant activity, reducing inflammation, and modulating the Akt/GSK-3β and Wnt-4/β-Catenin signaling pathways in male rats.
Conclusion: This study is the first to demonstrate the therapeutic effects of AVN-C therapy on DOX-induced liver damage in male rats. Therefore, AVN-C could have a pronounced palliative effect on the hepatotoxicity caused by DOX treatment. These findings suggest that AVN-C could potentially alleviate the hepatotoxicity associated with DOX-based chemotherapy.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antioxidants; avenanthramides; doxorubicin; hepatotoxicity; signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2024 Alwaili, Abu-Almakarem, Aljohani, Alkhodair, Al-Bazi, Eid, Alamri, Mobasher, Algarzae, A. Khayyat, Alshaygy and El-Said.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ahmed O. M., Elkomy M. H., Fahim H. I., Ashour M. B., Naguib I. A., Alghamdi B. S., et al. (2022). Rutin and quercetin counter doxorubicin-induced liver toxicity in Wistar rats via their modulatory effects on inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and Nrf2. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2710607. 10.1155/2022/2710607 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- AlAsmari A. F., Alharbi M., Alqahtani F., Alasmari F., AlSwayyed M., Alzarea S. I., et al. (2021). Diosmin alleviates doxorubicin-induced liver injury via modulation of oxidative stress-mediated hepatic inflammation and apoptosis via NfkB and MAPK pathway: a preclinical study. Antioxidants (Basel) 10 (12), 1998. 10.3390/antiox10121998 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

