Ultrasensitive protein-level detection for respiratory infectious viruses
- PMID: 39687610
- PMCID: PMC11646841
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1445771
Ultrasensitive protein-level detection for respiratory infectious viruses
Abstract
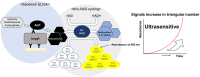
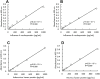
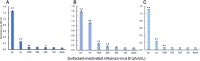
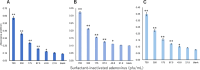
Influenza virus, adenovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus cause major respiratory infections. These infections have similar initial symptoms making it difficult to differentiate them based on symptoms alone. PCR is currently used as the standard diagnostic test for these infections, however, it has its limitations such as non-specific and false-negative amplifications, high cost, and the inability to distinguish between a live or dead virus. Therefore, there is a need for alternative diagnostic methods that focus on protein. Here, we introduce TN-cyclon™, which is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay combined with thio-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide cycling to amplify signals, rather than the protein itself. Using this method, we were able to detect extremely low levels of viruses such as influenza A, influenza B, adenovirus, and RS virus, with LODs of 2.96 × 10-18 moles/assay, 2.98 × 10-18 moles/assay, 2.36 × 10-18 moles/assay, and 3.55 × 10-18 moles/assay, respectively. Furthermore, we successfully detected viruses diluted with extract buffer, with a significant difference to the blank at concentrations of 3 pfu/mL for influenza A, 1000 pfu/mL for influenza B, 43.8 pfu/mL for adenovirus, and 125 pfu/mL for RS virus. This shows that our low-cost and easy-to-use technique has sufficient sensitivity in diagnosing respiratory infections.
Keywords: adenovirus; influenza virus; protein detection assay; respiratory syncytial virus; thio-NAD cycling; ultrasensitive ELISA.
Copyright © 2024 Kobayashi, Kyosei, Ogawa, Okita, Yoshimura and Ito.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors YKo, TY and EI declare a conflict of interest with BioPhenoMA Inc. YKo and EI have received honoraria from BioPhenoMA Inc. TY and EI have received research funding from BioPhenoMA Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Key Facts About Influenza (Flu). Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/keyfacts.htm (Accessed April 2, 2024).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Clinical Overview. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/adenovirus/hcp/clinical-overview.html (Accessed April 2, 2024).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Symptoms. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/adenovirus/symptoms.html (Accessed April 2, 2024).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . RSV Transmission. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/about/transmission.html (Accessed April 2, 2024).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Symptoms and Care. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/about/symptoms.html (Accessed April 2, 2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

