Myeloid response evaluated by noninvasive CT imaging predicts post-surgical survival and immune checkpoint therapy benefits in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39687612
- PMCID: PMC11646988
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1493735
Myeloid response evaluated by noninvasive CT imaging predicts post-surgical survival and immune checkpoint therapy benefits in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The potential of preoperative CT in the assessment of myeloid immune response and its application in predicting prognosis and immune-checkpoint therapy outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has not been explored.
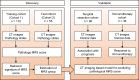
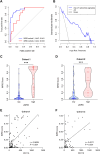
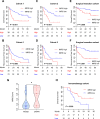
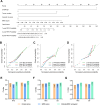
Methods: A total of 165 patients with pathological slides and multi-phase CT images were included to develop a radiomics signature for predicting the imaging-based myeloid response score (iMRS). Overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were assessed according to the iMRS risk group and validated in a surgical resection cohort (n = 98). The complementary advantage of iMRS incorporating significant clinicopathologic factors was investigated by the Cox proportional hazards analysis. Additionally, the iMRS in inferring the benefits of immune checkpoint therapy was explored in an immunotherapy cohort (n = 36).
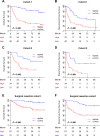
Results: We showed that AUCs of the optimal radiomics signature for iMRS were 0.941 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.909-0.973] and 0.833 (0.798-0.868) in the training and test cohorts, respectively. High iMRS was associated with poor RFS and OS. The prognostic performance of the Clinical-iMRS nomogram was better than that of a single parameter (p < 0.05), with a 1-, 3-, and 5-year C-index for RFS of 0.729, 0.709, and 0.713 in the training, test, and surgical resection cohorts, respectively. A high iMRS score predicted a higher proportion of objective response (vs. progressive disease or stable disease; odds ratio, 2.311; 95% CI, 1.144-4.672; p = 0.020; AUC, 0.718) in patients treated with anti-PD-1 and PD-L1.
Conclusions: iMRS may provide a promising method for predicting local myeloid immune responses in HCC patients, inferring postsurgical prognosis, and evaluating benefits of immune checkpoint therapy.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy; myeloid cells; prognosis; radiomics.
Copyright © 2024 Peng, Zhang, Li, Wang, Sun, Zhao, Pan, Zhang, Wu, Yu, Wu, Weng, Lin, Liu, Zhan, Xu, Zheng, Zhang and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A radiomics nomogram for the prediction of overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Nov 16;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00360-9. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33198809 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Deep learning-based CT radiomics predicts prognosis of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with TACE-HAIC combined with PD-1 inhibitors and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 21;25(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03555-7. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39838292 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of prognosis of immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with anti-angiogenic agents for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma by machine learning-based radiomics.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 19;25(1):888. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14247-0. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40389888 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning-based clinical-radiomics model predicting the treatment response of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs)-based conversion therapy in potentially convertible hepatocelluar carcinoma patients: a tumor marker prognostic study.Int J Surg. 2025 May 1;111(5):3342-3355. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002322. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 40085751 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Improve the Antitumor Effect of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 26;12:783236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783236. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899747 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current applications of radiomics in the assessment of tumor microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Apr 10. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04916-w. Online ahead of print. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40208284 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

