Serum cytokines as a biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitor toxicity in patients with pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 39687621
- PMCID: PMC11647018
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1480183
Serum cytokines as a biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitor toxicity in patients with pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
Background: Pleural mesothelioma (PM) is a rare cancer with a dismal prognosis. Dual immune checkpoint inhibitors have improved overall survival, but the rate of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) is high. Serum cytokines reflect systemic immune reactions and may serve as biomarkers for irAEs.
Patients and methods: Patients with pleural mesothelioma treated with nivolumab and ipilimumab with or without UV1 vaccine in the NIPU study were included. Serum cytokine levels were measured by Bio-Plex Pro Human Cytokine Screening 48-Plex Panel Assay. Correlations between cytokine levels and irAEs were analyzed by generalized linear mixed models to identify potential diagnostic and predictive biomarkers.
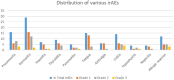
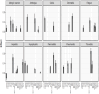
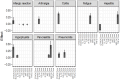
Results: Higher levels of MIG, eotaxin, MIP-1α, IP-10, TNF-α, MIP-1β, IL-4, MIF, IL-16, IL-2RA, SCGF.β and PDFG-BB at baseline are associated with increased risk of developing one or more irAEs. In particular, higher baseline levels of MIG are positively associated with thyroiditis and hypophysitis, and elevated levels of IP-10 and MIG to dermatitis. During the course of treatment, higher levels of MIG, eotaxin, MIF, TNF-α, MIP-1β, IL-4 and IL-16 are associated with an ongoing irAE. We found both predictive and diagnostic value of MIF with fatigue and of eotaxin with both colitis and pneumonitis. Higher levels of CTACK is associated with a lower risk of developing hepatitis, both before and after treatment.
Conclusions: Elevated levels of certain cytokines, both before and after onset of treatment, correlate with specific irAEs in PM patients receiving ICIs. These cytokines may be used as biomarkers to predict and detect irAES.
Keywords: biomarkers; checkpoint inhibition blockade; cytokines; immunotherapy; pleural mesothelioma.
Copyright © 2024 Farooqi, Zhao, Öjlert, Thunold, Juul, Bjaanæs, Horndalsveen, Nymoen, Helland and Haakensen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baas P, Scherpereel A, Nowak AK, Fujimoto N, Peters S, Tsao AS, et al. . First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable Malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2021) 397:375–86. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32714-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peters S, Scherpereel A, Cornelissen R, Oulkhouir Y, Greillier L, Kaplan MA, et al. . First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy in patients with unresectable Malignant pleural mesothelioma: 3-year outcomes from CheckMate 743. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:488–99. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.01.074 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aamdal E, Inderberg EM, Ellingsen EB, Rasch W, Brunsvig PF, Aamdal S, et al. . Combining a universal telomerase based cancer vaccine with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma - five-year follow up of a phase I/IIa trial. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:663865. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663865 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunsvig PF, Guren TK, Nyakas M, Steinfeldt-Reisse CH, Rasch W, Kyte JA, et al. . Long-term outcomes of a phase I study with UV1, a second generation telomerase based vaccine, in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:572172. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.572172 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

