Lactobacillus reuteri Alleviates Hyperoxia-Induced BPD by Activating IL-22/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Neonatal Mice
- PMID: 39687635
- PMCID: PMC11649352
- DOI: 10.1155/mi/4965271
Lactobacillus reuteri Alleviates Hyperoxia-Induced BPD by Activating IL-22/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Neonatal Mice
Abstract
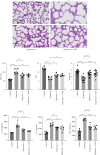
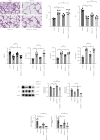
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most common chronic respiratory disease in preterm infants. Little is known about the regulatory effect of lung Lactobacillus and its mechanism in BPD. This study explored the effect of L. reuteri on hyperoxia-induced mice lung injuries and examined whether L. reuteri played a role via the IL-22/STAT3 pathway. We found that the intranasal administration of L. reuteri and its tryptophan metabolite indole-3-aldehyde (3-IAld) ameliorated hyperoxia-induced mice lung BPD-like changes, deceased proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α), and increased the levels of surfactant-associated protein C (SPC), aquaporin 5 (AQP5), and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2, also known as FLK-1). Furthermore, L. reuteri and 3-IAld increased the expression of IL-22. IL-22 was also confirmed to ameliorate hyperoxia-induced mice lung pathological changes, and the protective effects of L. reuteri could be inhibited by anti-IL-22 neutralizing antibody. Finally, we confirmed STAT3 activation by IL-22 in MLE-12 cells. In summary, our study confirmed L. reuteri alleviated hyperoxia-induced lung BPD-like changes in mice by activating the IL-22/STAT3 signaling pathway via IL-22 production. Probiotics Lactobacillus is a potential treatment for hyperoxia-induced lung injury in newborns.
Keywords: IL-22/STAT3 signaling pathway; L. reuteri; bronchopulmonary dysplasia; lung microbiota.
Copyright © 2024 Meiyu Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Speer C. P. Inflammation and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Seminars in Neonatology . 2003;8(1):29–38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

