A case report of PGAP2-related hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome in a Chinese family and literature review
- PMID: 39687712
- PMCID: PMC11646758
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1419976
A case report of PGAP2-related hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome in a Chinese family and literature review
Abstract
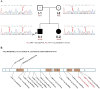
Recently, mutations have been identified in six genes (PIGA, PIGY, PIGO, PGAP2, PIGW and PGAP3) encoding proteins in the Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol(GPI)-anchor-synthesis pathway in individuals with hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome(HPMRS). Reports involving the rare pathogenic gene, post-GPI attachment to proteins 2 (PGAP2) are quite limited. In this study, we reported two patients with PGAP2 variants related neurodevelopmental disorders from Asian population. The proband, onset of epileptic spasms at 5 months, concurrently with global developmental dalay, facial malformation and elevated alkaline phosphatase. His younger sister, onset of epileptic spasms at 2 months, having similar clinical features as the proband. Their phenotypes are consistent with PGAP2 related diseases. The two missense variants [c.686C>T (p.Ala229Val) and c.677C>T (p.Thr226Ile)] in PGAP2 gene found in this family were segregation with the disease, while c.677C>T (p.Thr226Ile) was a novel variant. All the two patients showed a positive response to ACTH treatment and high-dose pyridoxine. In summary, this study contributes to expanding the pathogenic variant spectrum of PGAP2 related HPMRS, and provides new insights into the treatment.
Keywords: ACTH treatment; PGAP2 variants; epileptic spasms; facial malformation; hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome; pyridoxine.
© 2024 Pan, Ren, Chen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
BR, LC were employed by the company Shanghai Nyuen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

