Anatomy and histology of the olfactory organ of the javelin goby Synechogobius hasta (Gobiiformes, Gobiidae)
- PMID: 39688788
- PMCID: PMC11652435
- DOI: 10.1186/s42649-024-00105-z
Anatomy and histology of the olfactory organ of the javelin goby Synechogobius hasta (Gobiiformes, Gobiidae)
Abstract
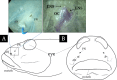
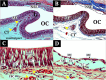
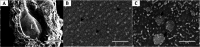
The olfactory organ of Synechogobius hasta was investigated with a focus on its environmental adaptation, using stereo microscopy and light microscopy. This research revealed the following anatomical and histological characteristics: (i) tubular anterior nostril, (ii) one longitudinal lamella, (iii) two accessory nasal sacs, (iv) lymphatic cells in the lower part of the sensory epithelium, (v) four to five villi of olfactory receptor neurons, (vi) abundant blood capillaries beneath the sensory epithelium, and (vii) rod-shaped erythrocytes. These findings hint that the olfactory organ of S. hasta has anatomical and histological adaptations to intertidal pools that undergo periodic hypoxia and increased temperature under stagnant water conditions due to the tidal cycle.
Keywords: Synechogobius; Anatomy; Erythrocyte; Histology olfactory organ; Nasal sac; Nostril; Tidal pool.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The author declares no competing interests relevant to the article.
Figures

References
-
- A.O. Kasumyan, The olfactory system in fish: structure, function, and role in behavior. J. Ichthyol. 44, S180 (2004)
-
- D.W. Hwang, S.O. Ryu, S.G. Kim, O.I. Choi, S.S. Kim, B.S. Koh, Geochemical characteristics of intertidal surface sediments along the southwestern coast of Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aqua Sci. 43, 146–158 (2010)
-
- E. Zeiske, B. Theisen, H. Breucker, Structure, development, and evolutionary aspects of the peripheral olfactory system, in Fish Chemoreception, ed. by T. J. Hara, Springer, Netherlands pp. 13–39 (1992)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
