Quantitative analysis of septin Cdc10 & Cdc3-associated proteome during stress response in the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 39689097
- PMCID: PMC11651612
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313444
Quantitative analysis of septin Cdc10 & Cdc3-associated proteome during stress response in the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
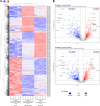
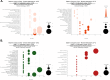
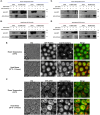
Cryptococcus neoformans is a pathogenic basidiomycetous yeast that primarily infects immunocompromised individuals. Fatal outcome of cryptococcosis depends on the ability of C. neoformans to sense and adapt to 37°C. A complex of conserved filament forming GTPases, called septins, composed of Cdc3, Cdc10, Cdc11, and Cdc12, assembles at the mother-bud neck in C. neoformans. Septins Cdc3 and Cdc12 are essential for proliferation of C. neoformans at 37°C and for virulence in the Galleria mellonella model of infection, presumably due to their requirement for septin complex formation, and the involvement in cytokinesis. However, how exactly Cdc3, and Cdc12 contribute to C. neoformans growth at 37°C remains unknown. Based on studies investigating roles of septins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, septin complex at the mother-bud neck of C. neoformans is predicted to interact with proteins involved in cell cycle control, morphogenesis, and cytokinesis, but the septin-associated proteome in C. neoformans has not been investigated. Here, we utilized tandem mass spectrometry to define C. neoformans proteins that associate with either Cdc3 or Cdc10 at ∼25°C or after the shift to 37°C. Our findings unveil a diverse array of septin-associated proteins, highlighting potential roles of septins in cell division, and stress response. Two proteins, identified as associated with both Cdc3 and Cdc10, the actin-binding protein profilin, which was detected at both temperatures, and ATP-binding multi-drug transporter Afr1, which was detected exclusively at 37°C, were further confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation. We also confirmed that association of Cdc3 with Afr1 was enhanced at 37°C. Upon shift to 37°C, septins Cdc3 and Cdc10 exhibited altered localization and Cdc3 partially co-localized with Afr1. In addition, we also investigated changes to levels of individual C. neoformans proteins upon shift from ∼25 to 37°C in exponentially grown culture and when cells entered stationary phase at ∼25°C. Our study reveals changes to C. neoformans proteome associated with heat and nutrient deprivation stresses and provides a landscape of septin-associated C. neoformans proteome, which will facilitate elucidating the biology of septins and mechanisms of stress response in this fungal pathogen.
Copyright: © 2024 Martinez Barrera et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Update of
-
Registered report protocol: Quantitative analysis of septin Cdc10-associated proteome in Cryptococcus neoformans.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 14;15(12):e0242381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242381. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. Update in: PLoS One. 2024 Dec 17;19(12):e0313444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313444. PMID: 33315917 Free PMC article. Updated.
Similar articles
-
Role of the anillin-like protein in growth of Cryptococcus neoformans at human host temperature.Fungal Genet Biol. 2022 May;160:103697. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2022.103697. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Fungal Genet Biol. 2022. PMID: 35472450 Free PMC article.
-
Registered report protocol: Quantitative analysis of septin Cdc10-associated proteome in Cryptococcus neoformans.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 14;15(12):e0242381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242381. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. Update in: PLoS One. 2024 Dec 17;19(12):e0313444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313444. PMID: 33315917 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Polyphosphatases have a polyphosphate-independent influence on the virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans.Infect Immun. 2025 Apr 8;93(4):e0007225. doi: 10.1128/iai.00072-25. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Infect Immun. 2025. PMID: 40071953 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Deletion of core septin gene aspB in Aspergillus fumigatus results in fungicidal activity of caspofungin.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 25:2025.02.25.640155. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.25.640155. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40060473 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Idnurm A, Bahn YS, Nielsen K, Lin X, Fraser JA, Heitman J. Deciphering the model pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3(10):753–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

