Microglial Mayhem NLRP3 Inflammasome's Role in Multiple Sclerosis Pathology
- PMID: 39690733
- PMCID: PMC11652677
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70135
Microglial Mayhem NLRP3 Inflammasome's Role in Multiple Sclerosis Pathology
Abstract
Introduction: This review delves into the intricate relationship between NLR inflammasomes, particularly the NLRP3 inflammasome, and the immune-mediated neurodegenerative disease, multiple sclerosis (MS). While the precise etiology of MS remains elusive, compelling research underscores the pivotal role of the immune response in disease progression. Notably, recent investigations highlight the significant involvement of NLRP3 inflammasomes in various autoimmune diseases, prompting an in-depth exploration of their impact on MS.
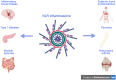
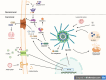
Method: The review focuses on elucidating the activation mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasomes within microglia/macrophages (MG/MФ), examining how this activation promotes an inflammatory response that exacerbates neuronal damage in MS. A comprehensive analysis of existing literature and research findings forms the basis for understanding the intricate interplay between NLRP3 inflammasomes and MS pathogenesis.
Results: Synthesizing current research, the review provides insight into the pivotal role played by NLR inflammasomes, specifically NLRP3, in MS. Emphasis is placed on the inflammatory response orchestrated by activated MG/MФ, elucidating the cascade that perpetuates neuronal damage in the disease.
Conclusions: This review concludes by consolidating key findings and offering a nuanced perspective on the role of NLRP3 inflammasomes in MS pathogenesis. The detailed exploration of the activation process within MG/MФ provides a foundation for understanding the disease's underlying mechanisms. Furthermore, the review sets the stage for potential therapeutic strategies targeting NLRP3 inflammasomes in the pursuit of MS treatment.
Keywords: NLRP3; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; inflammasome; macrophages; microglia; multiple sclerosis.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


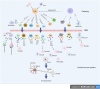


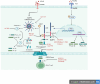
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 242103810034/Joint Fund of Henan Provincial Science and Technology R D Project
- 81801201/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024HLTJ08/Heluo Young Talents Support Program
- LJRC2024019/Henan Provincial Young and Middle-aged Health Science and Technology Innovation Leading Talent Training Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

