[Risk factors for decreased quality of life in patients with kidney stones predicted by the Chinese version of Wisconsin stone quality of life questionnaire]
- PMID: 39690772
- PMCID: PMC11652999
- DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.020
[Risk factors for decreased quality of life in patients with kidney stones predicted by the Chinese version of Wisconsin stone quality of life questionnaire]
Abstract
Objective: To assess health related quality of life (HRQOL) in patients with kidney stones and to predict risk factors for reduced HRQOL in the patients by the Chinese version of Wisconsin stone quality of life questionnaire (C-WISQOL).
Methods: The patients with renal stones admitted to Peking University People ' s Hospital from July 2020 to June 2021 were prospectively enrolled. The inclusion criteria included the patients with renal stones aged 18-80 years and sufficient Chinese language foundation, and the exclusion criteria included the patients with internal ureteral stents, malignant tumors, sepsis, etc. Demographic data and clinical data related to kidney stones were collected, and the C-WISQOL and the short form 36 health survey (SF-36) questionnaire completed by the patients was recorded. C-WISQOL included four domains (D): emotional impact (D1), social impact (D2), stone-related impact (D3) and vitality impact (D4). Cronbach ' s α coefficient was used to verify the internal consistency of C-WISQOL, Spearman ' s rho coefficient was used to verify the criterion validity between C-WISQOL and SF-36 questionnaire, confirmatory factor analysis was used to verify the structural validity, convergent validity and discrimination validity of C-WISQOL, and univariate and multivariate analyses were used to explore the risk factors leading to the decline of HRQOL in the patients with kidney stones.
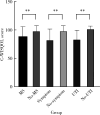
Results: The study included 307 patients with kidney stones, of whom 212 (69.1%) were male, with a mean age of (51.9±13.5) years, and a mean body mass index (BMI) of (25.4±3.6) kg/m2. 160 (52.1%) patients were complicated with metabolic syndrome (MS), 202 (65.8%) had history of calculi, 217 (70.7%) had calculi related symptoms, 53 (17.3%) had bilateral renal calculi, 82 (26.7%) had ureteral calculi, 199 (64.8%) had hydronephrosis, 78 (25.4%) had renal insufficiency, and urinary tract infection (UTI) was found in 168 patients (54.7%) with an average diameter of (15.6±5.9) mm. The mean total score of C-WISQOL questionnaire for all the patients was (94.9±13.7) points, D1 was (27.2±4.2) points, D2 was (23.8±3.7) points, D3 was (27.0±3.6) points, and D4 was (10.1±1.9) points. The Cronbach ' s α coefficient of the total score of C-WISQOL questionnaire was 0.968 and the four dimensions ranged from 0.860 to 0.898. The Spearman' s rho co- efficient between C-WISQOL and SF-36 total score was 0.564, and the Spearman' s rho coefficient between dimensions was 0.684-0.901, indicating that C-WISQOL had good internal consistency and criterion validity. Confirmatory factor analysis showed that C-WISQOL had good structural validity, convergent validity and discrimination validity. Univariate analysis showed that the patients with MS (OR=1.607, P < 0.001), calculi related symptoms (OR=1.268, P < 0.001), bilateral kidney stones (OR=1.900, P < 0.001), combined with ureteral calculi (OR=1.018, P < 0.001), accompanied by hydronephrosis (OR=1.685, P < 0.001), and UTI (OR=1.275, P < 0.001) were risk factors for decreased HRQOL in the patients with kidney stones, and multivariate analysis showed that the patients with MS (OR=1.475, P < 0.001), calculi related symptoms (OR=1.546, P=0.043) and UTI (OR=1.646, P=0.005) were independent risk factors for HRQOL decline in the patients with renal calculi. The t-test results showed that C-WISQOL scores were significantly higher in the patients without MS, stone-related symptoms and UTI than those in the patients with associated risk factors (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: C-WISQOL the questionnaire can be used to evaluate the HRQOL of patients with kidney stones with good reliability. The combination of MS, stone-related symptoms and UTI were independent risk factors for HRQOL reduction in the patients with renal stones.
目的: 使用中文版威斯康星结石生活质量问卷(Chinese version of Wisconsin stone quality of life questionnaire,C-WISQOL)评估肾结石患者的健康相关生活质量(health related quality of life,HRQOL),预测导致患者HRQOL降低的危险因素。
方法: 自2020年7月至2021年6月前瞻性纳入就诊于北京大学人民医院的肾结石患者,入组标准为18~80岁有足够汉语基础的肾结石患者,排除标准包括体内留置输尿管支架管的患者以及患有恶性肿瘤、脓毒症等的患者。收集患者的人口统计学资料和肾结石相关的临床资料,记录患者填写的C-WISQOL问卷和健康调查简表(short form 36 health survey, SF-36)。C-WISQOL包括四个维度(domain, D):情感影响(D1)、社会影响(D2)、结石相关影响(D3)和活力影响(D4)。使用Cronbach’ s α系数验证C-WISQOL的内部一致性,使用Spearman’ s rho系数验证C-WISQOL和SF-36之间的校标关联效度,使用验证性因子分析验证C-WISQOL的结构效度、聚合效度和区分效度,使用单因素和多因素分析探讨导致肾结石患者HRQOL下降的危险因素。
结果: 共纳入307例肾结石患者,其中212例(69.1%)为男性,平均年龄(51.9±13.5)岁,平均体重指数(body mass index,BMI) (25.4±3.6) kg/m2,160例(52.1%)患者合并代谢综合征(metabolic syndrome, MS),202例(65.8%)有既往结石病史,217例(70.7%)有结石相关症状,53例(17.3%)为双侧肾结石,82例(26.7%)合并输尿管结石,199例(64.8%)伴有肾积水,78例(25.4%)伴有肾功能不全,168例(54.7%)合并泌尿系感染(urinary tract infection, UTI),肾结石的平均直径为(15.6±5.9) mm。所有患者C-WISQOL问卷的平均总分为(94.9±13.7) 分,D1为(27.2±4.2) 分,D2为(23.8±3.7) 分,D3为(27.0±3.6) 分,D4为(10.1±1.9) 分。C-WISQOL问卷总分的Cronbach’ s α系数为0.968,四个维度为0.860~0.898。C-WISQOL和SF-36问卷总分相关性的Spearman’ s rho系数为0.564,维度间相关性为0.684~0.901,表明C-WISQOL有较好的内部一致性和校标关联效度。验证性因子分析显示,C-WISQOL具有较好的结构效度、聚合效度和区分效度。单因素分析显示,合并MS(OR=1.607,P < 0.001)、有结石相关症状(OR=1.268,P < 0.001)、双侧肾结石(OR=1.900,P < 0.001)、合并输尿管结石(OR=1.018,P < 0.001)、伴有肾积水(OR=1.685,P < 0.001)、伴有UTI(OR=1.275,P < 0.001)是肾结石患者HRQOL降低的危险因素;多因素分析表明,合并MS(OR=1.475,P < 0.001)、合并输尿管结石(OR=1.546,P=0.043)、伴有UTI(OR=1.646,P=0.005)是肾结石患者HRQOL下降的独立危险因素。t检验结果显示,无MS、结石相关症状和UTI患者的C-WISQOL得分均显著高于合并相关危险因素组(P < 0.001)。
结论: C-WISQOL问卷可用于评估肾结石患者的HRQOL,具有较好的可靠性。合并MS、结石相关症状和UTI是肾结石患者HRQOL降低的独立危险因素。
Keywords: Chinese version of Wisconsin stone quality of life questionnaire; Kidney calculi; Quality of life; Risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Streeper NM, Galida M, Boltz S, et al. Is stone-free status after surgical intervention for kidney stones associated with better health-related quality of life? A multicenter study from the North American Stone Quality of Life Consortium. Urology. 2021;148:77–82. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.09.058. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources