SIRT1/NOX1 pathway mediated ameliorative effects of rosmarinic acid in folic acid-induced renal injury
- PMID: 39691298
- PMCID: PMC11648342
- DOI: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_213_23
SIRT1/NOX1 pathway mediated ameliorative effects of rosmarinic acid in folic acid-induced renal injury
Abstract
Background and purpose: Renal injury is a serious disorder that can be caused by some diseases or agents. Rosmarinic acid (RA) is a natural and safe compound with powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In this study, the ameliorative effects of RA were assayed in folic acid (FA)-induced renal injury by involving the SIRT1/NOX1 pathway.
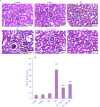
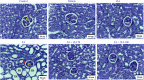
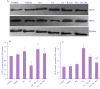
Experimental approach: Thirty-six male C57/BL6 mice were divided into 6 groups (n = 6) including control, vehicle, FA, RA, FA + RA 50, and FA + RA 100. After 10 days, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and oxidative stress were measured. The expression of SIRT1 and NOX1 proteins was evaluated by western blot. Also, histopathological alterations were assayed by H&E and PAS staining methods.
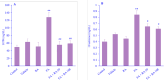
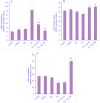
Findings/results: BUN and creatinine were significantly higher in the FA group compared to the control group; however, their levels decreased after RA treatment in both doses. A significant decrease was observed in swelling, necrosis, and desquamation of tubular epithelial cells in the FA + RA 50 and FA + RA 100 groups compared to the FA group. RA in the animals receiving FA increased SIRT1 expression and the levels of GSH and SOD compared to the FA group. RA in the animals receiving FA showed a significant decrease in NOX1 expression and MDA level compared to the FA group.
Conclusion and implications: The findings declared that the administration of RA has positive effects against renal damage induced by FA. The effect might result from involvement in the SIRT1/NOX1 pathway and thereby attenuation of oxidative stress.
Keywords: Folic acid; NOX1; Renal failure; Rosmarinic acid; SIRT1.
Copyright: © 2024 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Mahadevan V. Anatomy of the kidney and ureter. Surgery (Oxford) 2019;37(7):359–364. DOI: 10.1016/j.mpsur.2019.04.005.
-
- Goossens JF, Thuru X, Bailly C. Properties and reactivity of the folic acid and folate photoproduct 6-formylpterin. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;171:1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.05.002. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
