Comprehensive review on Alzheimer's disease: From the posttranslational modifications of Tau to corresponding treatments
- PMID: 39691421
- PMCID: PMC11649392
- DOI: 10.1002/ibra.12176
Comprehensive review on Alzheimer's disease: From the posttranslational modifications of Tau to corresponding treatments
Abstract
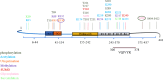
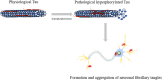
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease, which is mainly characterized by the abnormal deposition of β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) and Tau. Since Tau aggregation is more closely associated with synaptic loss, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline than Aβ, the correlation between Tau and cognitive function in AD has gradually gained attention. The posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of Tau are key factors contributing to its pathological changes, which include phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, glycation, small ubiquitin-like modifier mediated modification (SUMOylation), methylation, succinylation, etc. These modifications change the structure of Tau, regulating Tau microtubule interactions, localization, degradation, and aggregation, thereby affecting its propensity to aggregate and leading to neuronal injury and cognitive impairments. Among numerous PTMs, drug development based on phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and SUMOylation primarily involves enzymatic reactions, affecting either the phosphorylation or degradation processes of Tau. Meanwhile, methylation, glycosylation, and succinylation are associated with maintaining the structural stability of Tau. Current research is more extensive on phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and methylation, with related drugs already developed, particularly focusing on phosphorylation and ubiquitination. In contrast, there is less research on SUMOylation, glycosylation, and succinylation, requiring further basic research, with the potential to become novel drug targets. In conclusion, this review summarized the latest research on PTMs of Tau and related drugs, highlighting the potential of targeting specific PTMs for developing novel therapeutic strategies in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Tau; post‐translational modifications; treatments.
© 2024 The Author(s). Ibrain published by Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University and Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
