Effects of Ficus exasperata on neurotransmission and expression of BDNF, tau, ACHE and BACE in diabetic rats
- PMID: 39691470
- PMCID: PMC11650316
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2024.100333
Effects of Ficus exasperata on neurotransmission and expression of BDNF, tau, ACHE and BACE in diabetic rats
Abstract
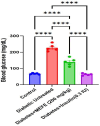
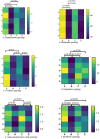
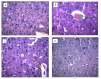
Diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder, has significant global health implications, particularly due to its neurological complications, such as diabetic neuropathy. This condition increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases by affecting peripheral nerves and cognition. Ficus exasperata, known for its neuroprotective properties, shows promise as a therapeutic option for addressing these complications. This study evaluates the effects of methanol extract of Ficus exasperata (MEFE) on neurotransmission and the expression of Tau, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), acetylcholinesterase (ACHE), and Beta-Site Amyloid Precursor Protein Cleaving Enzyme (BACE) in alloxan-induced diabetic Wistar rats. The controlled experimental design involved 20 Wistar rats divided into four groups (n = 5): control, diabetic untreated, diabetes + MEFE (200 mg/kg), and diabetes + insulin (0.3 IU). The methanol extract was prepared using cold maceration, and an aliquot was subjected to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Constituents of MEFE were docked with neurologic receptors. Blood glucose levels were measured using the glucose oxidase method, and neurotransmitter levels, antioxidants, oxidative stress markers, and the expression of Tau, BDNF, ACHE, and BACE were assessed using standard procedures and qRT-PCR. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA at P < 0.05. Results indicated that MEFE significantly reduced fasting blood glucose levels compared to untreated diabetic rats. In silico docking identified kaur-16-ene, a constituent of MEFE, as having the highest binding affinity for NMDA, TrkB, mAchR and nAchR receptors, indicating its neuroprotective potential. MEFE also enhanced antioxidant enzyme levels (SOD, GPx, catalase) while reducing oxidative stress markers (MDA, 8-OHdG). Gene expression analysis revealed that MEFE modulates the expression of Tau, BDNF, ACHE, and BACE, suggesting its potential to influence neurodegenerative pathways associated with diabetic neuropathy. Ficus exasperata demonstrates significant therapeutic potential in managing diabetic neuropathy and related cognitive impairments by modulating neurotransmission, protein expression, and antioxidant defenses.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Ficus exasperata, neurotransmission; Kaur-16-ene; Neuroprotective properties.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021. with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 [published correction appears in Lancet. 2023 Sep 30;402:1132. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02044-5. 10408. Lancet. 2023;402(10397):203-234. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

