A new perspective on macrophage-targeted drug research: the potential of KDELR2 in bladder cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 39691708
- PMCID: PMC11649672
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485109
A new perspective on macrophage-targeted drug research: the potential of KDELR2 in bladder cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
Introduction: Bladder cancer was recognized as one of the most common malignant tumors in the urinary system, and treatment options remained largely limited to conventional surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, which limited patient benefits.
Methods: Researchers constructed an RNA transcriptome map of bladder cancer by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing and clinical data, identifying potential molecular targets for diagnosis and treatment. We also verified the antitumor activity of the target through in vitro experiment.
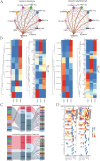
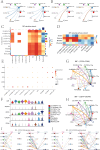
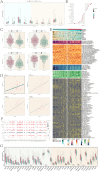
Results: A distinct tumor cell subpopulation characterized by elevated S100A8 expression exhibited high copy number variation, high stemness, and low differentiation. It interacted with myeloid cells via the MIF-(CD74+CD44) and MIF-(CD74+CXCR4) signaling pathways. This study underscored KDELR2's role in promoting cell proliferation, invasion, and migration, providing new therapeutic insights. Prognostic analysis revealed that KDELR2 correlated with poor survival, higher immune scores, and increased macrophage infiltration.
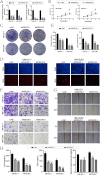
Discussion: The findings suggested that patients with high KDELR2 expression might benefit from immune checkpoint therapy. KDELR2 was also shown to enhance bladder cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration, highlighting it as a promising target for macrophage-focused drug development.
Keywords: KDELR2; S100A8; TCs; bladder cancer; macrophage.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Jia, Sun, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of macrophage-related genes in prostate cancer by integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 24;16(8):6809-6838. doi: 10.18632/aging.205727. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38663915 Free PMC article.
-
Co-inhibition of PGF and VEGFA enhances the effectiveness of immunotherapy in bladder cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Oct 28;21(15):2870-2882. doi: 10.7150/ijms.100957. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39628692 Free PMC article.
-
IGF2BP2 Shapes the Tumor Microenvironment by Regulating Monocyte and Macrophage Recruitment in Bladder Cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Dec;13(24):e70506. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70506. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39711402 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-associated macrophages in bladder cancer: roles and targeted therapeutic strategies.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 13;15:1418131. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1418131. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39606239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Molecular Therapeutics for Bladder Cancer-A New Option beyond the Mixed Fortunes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 1;21(19):7268. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197268. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33019653 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signalling pathways and cellular functions of KDEL receptors: implications in cancer biology.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Aug 6;82(1):299. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05820-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40767982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

