Role of rapidly evolving immunotherapy in chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease
- PMID: 39691713
- PMCID: PMC11649625
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1451977
Role of rapidly evolving immunotherapy in chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease
Abstract
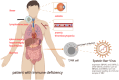
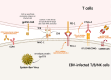
Chronic active Epstein-Barr Virus disease is a kind of Epstein-Barr Virus associated T/NK cell lymphoproliferative disease. At present, there is still a lack of standard therapeutic regimen for its treatment, but its basic treatment principles include controlling inflammatory response, anti-tumor proliferation, and immune reconstitution. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is currently the only method that can cure this disease. In recent years, immunotherapy has developed rapidly and is widely used in the treatment of various hematological malignancies; various immunotherapy drugs, including PD-1 inhibitors, have also demonstrated their safety and efficacy in CAEBV, while immune cell therapies such as Epstein- Barr virus-specific T cells have also displayed their unique advantages in CAEBV.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; Epstein-Barr virus specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes; PD-1 inhibitor; chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2024 Yan, Ming, Zhu and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

