Development of a sensitive disease-screening model using comprehensive circulating microRNA profiles in dogs: A pilot study
- PMID: 39691815
- PMCID: PMC11647647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vas.2024.100414
Development of a sensitive disease-screening model using comprehensive circulating microRNA profiles in dogs: A pilot study
Abstract
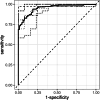
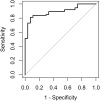
In the veterinary field, the utility of disease-identification models that use comprehensive circulating microRNA (miRNA) profiles produced through measurements based on next-generation sequencing (NGS) remains unproven. To integrate NGS technology with automated machine learning (autoML) to create a comprehensive circulating miRNA profile and to assess the clinical utility of a disease-screening model derived from this profile. The study involved dogs diagnosed with or being treated for various diseases, including tumors, across multiple veterinary clinics (n = 254), and healthy dogs without apparent diseases (n = 91). miRNA was extracted from EDTA-treated plasma, and a comprehensive analysis was conducted of one million reads per sample using NGS. Then autoML technology was applied to develop a diagnostic model based on miRNA. Among these models, the one with the highest performance was chosen for evaluation. The diagnostic model, based on the comprehensive circulating miRNA profile developed in this study, achieved an AUC score of 0.89, with a sensitivity of 85 % and a specificity of 88 % for the disease samples. The miRNA-based diagnostic model demonstrated high sensitivity for disease groups and has the potential to be an effective screening test. This study indicates that a comprehensive miRNA profile in dog plasma could serve as a highly sensitive blood biomarker.
Keywords: Automated machine learning; Canine; Next-generation sequencing; microRNA.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Kohei Omura reports a relationship with Arkray Marketing Inc that includes: employment. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of hepatocellular carcinoma miRNA expression profiling as evaluated by next generation sequencing and microarray.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 12;9(9):e106314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106314. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25215888 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of the Anticoagulant Type in Blood Collection Tubes on Circulating Extracellular Plasma MicroRNA Profiles Revealed by Small RNA Sequencing.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 7;23(18):10340. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810340. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142259 Free PMC article.
-
SIV Infection Regulates Compartmentalization of Circulating Blood Plasma miRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) and Extracellular Condensates (ECs) and Decreases EV-Associated miRNA-128.Viruses. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):622. doi: 10.3390/v15030622. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992331 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA panels as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 7;9:915226. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.915226. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36419785 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MicroRNA as Potential Source for Neurodegenerative Diseases Biomarkers.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;52(3):1494-1503. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8944-x. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25367880 Review.
References
-
- Campbell J.D., Liu G., Luo L., Xiao J., Gerrein J., Juan-Guardela B., Tedrow J., Alekseyev Y.O., Yang I.V., Correll M., Geraci M., Quackenbush J., Sciurba F., Schwartz D.A., Kaminski N., Johnson W.E., Monti S., Spira A., Beane J., Lenburg M.E. Assessment of microRNA differential expression and detection in multiplexed small RNA sequencing data. RNA (New York, N.Y.), 2015;21(2):164–171. doi: 10.1261/rna.046060.114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

