Cytokine expression and cytokine-mediated cell-cell communication during skeletal muscle regeneration revealed by integrative analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data
- PMID: 39691872
- PMCID: PMC11647049
- DOI: 10.1002/ccs3.12055
Cytokine expression and cytokine-mediated cell-cell communication during skeletal muscle regeneration revealed by integrative analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data
Abstract
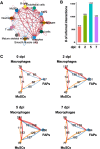
Skeletal muscles undergo self-repair upon injury, owing to the resident muscle stem cells and their extensive communication with the microenvironment of injured muscles. Cytokines play a critical role in orchestrating intercell communication to ensure successful regeneration. Immune cells as well as other types of cells in the injury site, including muscle stem cells, are known to secret cytokines. However, the extent to which various cell types express distinct cytokines and how the secreted cytokines are involved in intercell communication during regeneration are largely unknown. Here we integrated 15 publicly available single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets of mouse skeletal muscles at early regeneration timepoints (0, 2, 5, and 7 days after injury). The resulting dataset was analyzed for the expression of 393 annotated mouse cytokines. We found widespread and dynamic cytokine expression by all cell types in the regenerating muscle. Interrogating the integrated dataset using CellChat revealed extensive, bidirectional cell-cell communications during regeneration. Our findings provide a comprehensive view of cytokine signaling in the regenerating muscle, which can guide future studies of ligand-receptor signaling and cell-cell interaction to achieve new mechanistic insights into the regulation of muscle regeneration.
Keywords: cell–cell communication; cytokines; muscle stem cells; scRNA‐seq; skeletal muscle regeneration.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

