Role for the PIP2-binding protein myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate in vascular tissue: A novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 39691873
- PMCID: PMC11647048
- DOI: 10.1002/ccs3.12052
Role for the PIP2-binding protein myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate in vascular tissue: A novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease
Abstract
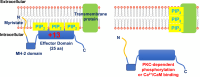
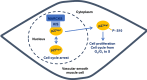
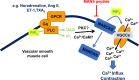
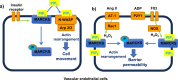
In vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and vascular endothelial cells (VECs), phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) acts as a substrate for phospholipase C (PLC)- and phosphoinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-mediated signaling pathways and an unmodified ligand at ion channels and other macromolecules, which are key processes in the regulation of cell physiological and pathological phenotypes. It is envisaged that these distinct roles of PIP2 are achieved by PIP2-binding proteins, which act as PIP2 buffers to produce discrete pools of PIP2 that permits targeted release within the cell. This review discusses evidence for the expression, cell distribution, and role of myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS), a PIP2-binding protein, in cellular signaling and function of VSMCs. The review indicates the possibilities for MARCKS as a therapeutic target for vascular disease involving dysfunctional cell proliferation and migration, endothelial barrier permeability, and vascular contractility such as atherosclerosis, systemic and pulmonary hypertension, and sepsis.
Keywords: MARCKS; PIP2; contractility; migration; permeability; proliferation; vascular endothelial cells; vascular smooth muscle cells.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MARCKS mediates vascular contractility through regulating interactions between voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and PIP2.Vascul Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;132:106776. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2020.106776. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Vascul Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32707323 Free PMC article.
-
Myristoylated Alanine-Rich Protein Kinase Substrate (MARCKS) Regulates Small GTPase Rac1 and Cdc42 Activity and Is a Critical Mediator of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Migration in Intimal Hyperplasia Formation.J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 Oct 8;4(10):e002255. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002255. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015. PMID: 26450120 Free PMC article.
-
Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) produces reversible inhibition of phospholipase C by sequestering phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in lateral domains.J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 18;271(42):26187-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.42.26187. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8824266
-
The MARCKS family of phospholipid binding proteins: regulation of phospholipase D and other cellular components.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;82(1):191-200. doi: 10.1139/o03-087. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15052337 Review.
-
PIP2: A critical regulator of vascular ion channels hiding in plain sight.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 25;117(34):20378-20389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2006737117. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32764146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Logothetis, D. E. , Petrou V. I., Zhang M., Mahajan R., Meng X.‐Y., Adney S. K., Cui M., and Baki L.. 2015. “Phosphoinositide Control of Membrane Protein Function: A Frontier Led by Studies on Ion Channels.” Annual Review of Physiology 77(1): 81–104. 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170358. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

