TAC1b mutation in Candida auris decreases manogepix susceptibility owing to increased CDR1 expression
- PMID: 39692503
- PMCID: PMC11823642
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01508-24
TAC1b mutation in Candida auris decreases manogepix susceptibility owing to increased CDR1 expression
Abstract
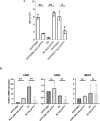
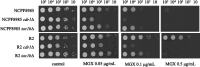
Candida auris is an emerging pathogenic fungus that is highly resistant to existing antifungal drugs. Manogepix is a novel antifungal agent that exerts antifungal activity by inhibiting glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis. Although the mechanisms of resistance of Candida species to manogepix have been reported previously, those of C. auris are yet to be studied. To investigate the resistance mechanisms of C. auris, we exposed a clinical isolate (clade I) to manogepix in vitro and generated strains with reduced susceptibility to manogepix. A search for gain-of-function mutations that upregulate efflux pump expression confirmed the presence of the D865N amino acid mutation in TAC1b. We used the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-Cas9 system to create a recovery strain (N865D) in which only this single nucleotide mutation was returned to the wild-type sequence. We generated a mutant strain by introducing only the D865N mutation into the parent strain and a different clade strain (clade III). The D865N mutant strains were clearly less susceptible to manogepix than the parental strains and exhibited high CDR1 expression. Moreover, we generated a strain deficient in CDR1 and confirmed that this strain had significantly increased susceptibility to manogepix. Thus, the present study demonstrated that the TAC1b mutation in C. auris upregulates CDR1 expression and decreases its susceptibility to manogepix.
Keywords: CDR1; CRISPR-Cas9; Candida auris; TAC1b; antifungal resistance; efflux pumps; manogepix.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Vazquez JA, Pappas PG, Boffard K, Paruk F, Bien PA, Tawadrous M, Ople E, Wedel P, Oborska I, Hodges MR. 2023. Clinical efficacy and safety of a novel antifungal, fosmanogepix, in patients with candidemia caused by Candida auris: results from a phase 2 trial. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 67:e0141922. doi:10.1128/aac.01419-22 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pappas PG, Vazquez JA, Oren I, Rahav G, Aoun M, Bulpa P, Ben-Ami R, Ferrer R, Mccarty T, Thompson GR, Schlamm H, Bien PA, Barbat SH, Wedel P, Oborska I, Tawadrous M, Hodges MR. 2023. Clinical safety and efficacy of novel antifungal, fosmanogepix, for the treatment of candidaemia: results from a phase 2 trial. J Antimicrob Chemother 78:2471–2480. doi:10.1093/jac/dkad256 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Watanabe NA, Miyazaki M, Horii T, Sagane K, Tsukahara K, Hata K. 2012. E1210, a new broad-spectrum antifungal, suppresses Candida albicans hyphal growth through inhibition of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:960–971. doi:10.1128/AAC.00731-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

