A large-scale proteomics resource of circulating extracellular vesicles for biomarker discovery in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 39693144
- PMCID: PMC11655061
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.87369
A large-scale proteomics resource of circulating extracellular vesicles for biomarker discovery in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
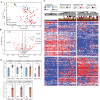
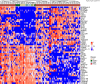
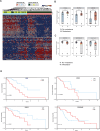
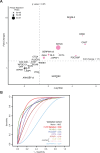
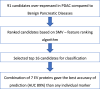
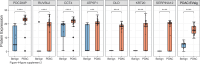
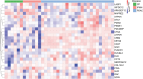
Pancreatic cancer has the worst prognosis of all common tumors. Earlier cancer diagnosis could increase survival rates and better assessment of metastatic disease could improve patient care. As such, there is an urgent need to develop biomarkers to diagnose this deadly malignancy. Analyzing circulating extracellular vesicles (cEVs) using 'liquid biopsies' offers an attractive approach to diagnose and monitor disease status. However, it is important to differentiate EV-associated proteins enriched in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) from those with benign pancreatic diseases such as chronic pancreatitis and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN). To meet this need, we combined the novel EVtrap method for highly efficient isolation of EVs from plasma and conducted proteomics analysis of samples from 124 individuals, including patients with PDAC, benign pancreatic diseases and controls. On average, 912 EV proteins were identified per 100 µL of plasma. EVs containing high levels of PDCD6IP, SERPINA12, and RUVBL2 were associated with PDAC compared to the benign diseases in both discovery and validation cohorts. EVs with PSMB4, RUVBL2, and ANKAR were associated with metastasis, and those with CRP, RALB, and CD55 correlated with poor clinical prognosis. Finally, we validated a seven EV protein PDAC signature against a background of benign pancreatic diseases that yielded an 89% prediction accuracy for the diagnosis of PDAC. To our knowledge, our study represents the largest proteomics profiling of circulating EVs ever conducted in pancreatic cancer and provides a valuable open-source atlas to the scientific community with a comprehensive catalogue of novel cEVs that may assist in the development of biomarkers and improve the outcomes of patients with PDAC.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer biology; extracellular vesicles; human; pancreatic cancer; pancreatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
BB, LM, LH, WT, MH, AI, SM Inventor on a pending patent application (US20220291222A1) for pancreatic cancer detection, based on data generated from this publication, MH, CM, LT, RG, JW, AB, RB, SP, MS, SF No competing interests declared, JG Employee of Agenus Inc, SN Employee of Deciphera Pharmaceuticals
Figures





Update of
-
A Large-Scale Proteomics Resource of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles for Biomarker Discovery in Pancreatic Cancer.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 19:2023.03.13.23287216. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.13.23287216. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Dec 18;12:RP87369. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87369. PMID: 36993200 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR, Winchester DP. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA. 2017;67:93–99. doi: 10.3322/caac.21388. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B. 1995;57:289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x. - DOI
-
- Castillo J, Bernard V, San Lucas FA, Allenson K, Capello M, Kim DU, Gascoyne P, Mulu FC, Stephens BM, Huang J, Wang H, Momin AA, Jacamo RO, Katz M, Wolff R, Javle M, Varadhachary G, Wistuba II, Hanash S, Maitra A, Alvarez H. Surfaceome profiling enables isolation of cancer-specific exosomal cargo in liquid biopsies from pancreatic cancer patients. Annals of Oncology. 2018;29:223–229. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

