Paracentrotus lividus sea urchin gonadal extract mitigates neurotoxicity and inflammatory signaling in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39693313
- PMCID: PMC11654954
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315858
Paracentrotus lividus sea urchin gonadal extract mitigates neurotoxicity and inflammatory signaling in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
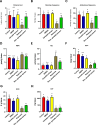
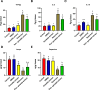
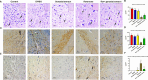
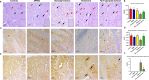
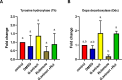
The present study investigates the neuroprotective effects of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus gonadal extract on rotenone-induced neurotoxicity in a Parkinson's disease (PD) rat model. Parkinson's disease, characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN), is exacerbated by oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. The study involved fifty Wistar rats divided into five groups: control, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) control, Paracentrotus lividus gonadal extract-treated, rotenone-treated, and combined rotenone with Paracentrotus lividus gonadal extract-treated. Behavioral assessments included the rotarod and open field tests, while biochemical analyses measured oxidative stress markers (malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), glutathione (GSH)), antioxidants (superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT)), pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)), and neurotransmitters (dopamine (DA), levodopa (L-Dopa)). Histological and immunohistochemical analyses evaluated the neuronal integrity and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and alpha-synuclein expression. The results showed that Paracentrotus lividus gonadal extract significantly mitigated rotenone-induced motor deficits and improved locomotor activity. Biochemically, the extract reduced oxidative stress and inflammation markers while enhancing antioxidant levels. Histologically, it restored neuronal integrity and reduced alpha-synuclein accumulation. Molecularly, it increased tyrosine hydroxylase and dopa decarboxylase gene expression, essential for dopamine synthesis. These findings suggest that Paracentrotus lividus gonadal extract exerts neuroprotective effects by modulating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and dopaminergic neuron integrity, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for Parkinson's disease.
Copyright: © 2024 Nagy et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Supplements of Ginkgo biloba Extract Alleviate Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Impairments and Neurotoxicity in Rotenone-Induced Parkinsonian Rats.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020;21(12):1259-1268. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666200320135849. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32196446
-
Lycopodium Attenuates Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Molecules. 2019 Jun 10;24(11):2182. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112182. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31185705 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Thymol, a Dietary Monoterpene Against Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Rotenone-Induced Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 27;20(7):1538. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071538. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30934738 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain activation and progression of inflammatory cycles in Parkinson's disease.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Jan 13;27(1):20. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2701020. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 35090325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptin as a potential neuroprotective target in Parkinson's Disease: Exploring its role in Neuroinflammation, oxidative Stress, and dopaminergic neurodegeneration.Neuroscience. 2025 Apr 19;572:134-144. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2025.03.008. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 40064367 Review.
References
-
- Manoharan S, Guillemin GJ, Abiramasundari RS, Essa MM, Akbar M, Akbar MD. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Huntington’s Disease: A Mini Review. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2016;2016:8590578. doi: 10.1155/2016/8590578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, Halliday GM, Brundin P, Volkmann J, et al.. Parkinson disease. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2017;3(1):17013. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

